
Types of Electric Motors and Their Applications
Electric motors are essential devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, making them a key component in household appliances, industrial machinery, transportation, and renewable energy systems. Their design and operation vary based on power source, rotation control, and efficiency.
Classification of Electric Motors
Electric motors are classified based on:
✔ Power supply type - AC or DC
✔ Synchronization with the power source - Synchronous or asynchronous
✔ Rotor and stator design - Induction, brushed, or brushless
There are two primary categories of electric motors:
1️⃣ DC (Direct Current) Motors - Powered by batteries, solar panels, or rectified AC sources
2️⃣ AC (Alternating Current) Motors - Powered by household and industrial power grids
DC Motors (Direct Current Motors)
DC motors operate using direct current and provide precise control over speed and torque, making them ideal for applications requiring variable speed.
Types of DC Motors
Brushed DC Motors:
✔ Equipped with a brush-commutator system
✔ Lower efficiency due to friction and wear
✔ Used in automotive applications, household appliances, and industrial tools
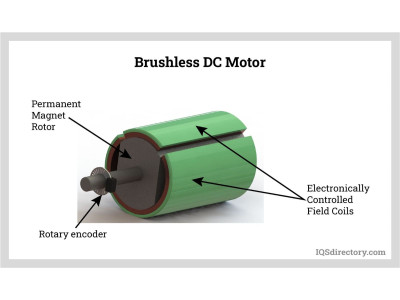
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC):
✔ Uses electronic commutation instead of brushes
✔ Higher efficiency, lower maintenance
✔ Found in electric vehicles, drones, and computer cooling fans
Series-Wound DC Motors:
✔ High starting torque
✔ Used in cranes, elevators, and electric trains
Shunt-Wound DC Motors:
✔ Constant speed operation
✔ Used in industrial machinery and conveyors
Compound DC Motors:
✔ Combines series and shunt characteristics
✔ Provides high torque and steady speed
✅ Advantages of DC Motors:
✔ High starting torque
✔ Precise speed control
✔ Compact and efficient
❌ Disadvantages:
✘ Require more maintenance (brushed motors)
✘ Higher cost than AC motors
Common Applications:
✔ Electric vehicles (EVs)
✔ Power tools (drills, saws, grinders)
✔ Industrial robots and actuators
AC Motors (Alternating Current Motors)
AC motors dominate the market due to their versatility, reliability, and efficiency. They are found in household appliances, HVAC systems, and industrial automation.
Types of AC Motors
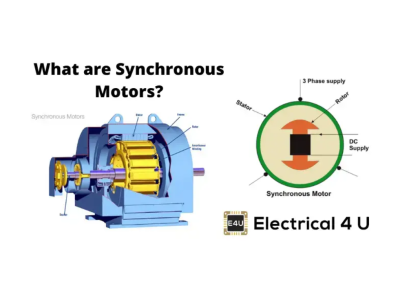
Synchronous AC Motors:
✔ Operate at a fixed speed synchronized with the power frequency
✔ Available in high-power applications
✔ Used in compressors, generators, and large ventilation systems
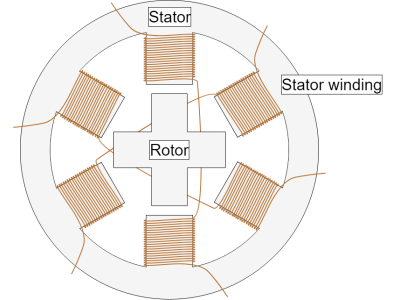
Induction (Asynchronous) Motors:
✔ Most widely used motor type
✔ Operates below synchronous speed
✔ Divided into single-phase and three-phase motors
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Induction Motors
| Feature | Single-Phase Motor | Three-Phase Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Single-phase (120V or 240V) | Three-phase (208V, 480V, etc.) |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Usage | Small appliances, fans, pumps | Industrial machines, heavy equipment |
| Starting Mechanism | Requires capacitors | Self-starting |
✅ Advantages of Induction Motors:
✔ Simple & durable - No brushes or commutators
✔ High efficiency - Lower power losses
✔ Low maintenance - Ideal for industrial use
❌ Disadvantages:
✘ Speed control is limited (requires a frequency converter)
✘ Lower starting torque than DC motors
Common Applications:
✔ Fans, refrigerators, and washing machines
✔ HVAC systems and compressors
✔ Industrial pumps and conveyor belts
Specialized Electric Motors
Universal Motors:
✔ Operates on both AC and DC power
✔ High-speed rotation (over 3000 RPM)
✔ Found in blenders, vacuum cleaners, and power tools
Stepper Motors:
✔ Precise position control
✔ Used in 3D printers, CNC machines, and robotics
Servo Motors:
✔ High-performance closed-loop control
✔ Used in robotics, CNC machinery, and aerospace applications
Comparison: DC vs. AC Motors
| Feature | DC Motor | AC Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Direct Current (Battery/Solar) | Alternating Current (Grid) |
| Speed Control | Excellent | Limited |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance | Higher (brushed motors) | Low |
| Best Used For | Precision applications | Industrial applications |
Choosing the Right Motor for Your Application
For Home Appliances:
✔ Single-phase AC induction motors for refrigerators, washing machines, and fans
✔ Universal motors for blenders and vacuum cleaners
For Industrial Use:
✔ Three-phase induction motors for conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors
✔ Synchronous motors for heavy-duty machinery
For Robotics & Automation:
✔ DC motors for precise control and flexibility
✔ Stepper motors for position accuracy
FAQ: Electric Motors
1️⃣ What type of motor is used in electric cars?
✅ Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) or Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) are commonly used in electric vehicles due to high efficiency and reliability.
2️⃣ Why are AC motors preferred for industrial applications?
✅ AC motors are more efficient, durable, and require less maintenance than DC motors. They are also cost-effective for large-scale operations.
3️⃣ Can a single-phase motor run industrial machines?
❌ No, three-phase motors are recommended for industrial use as they offer higher power output and efficiency.
4️⃣ What is the main disadvantage of DC motors?
❌ Higher maintenance due to brushes (in brushed DC motors) and complex speed control compared to AC motors.
5️⃣ Are induction motors better than synchronous motors?
✅ Induction motors are cheaper, more durable, and self-starting, while synchronous motors offer precise speed control and higher efficiency in constant load applications.
Final Thoughts: Understanding Electric Motors
Electric motors are a crucial component of modern technology, powering everything from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Key Takeaways:
✔ DC motors provide precise speed control but need more maintenance
✔ Induction motors are cost-effective and reliable for industrial applications
✔ Synchronous motors maintain constant speed and work efficiently for high-power systems
✔ Universal motors offer versatility in household appliances
⚡ Choosing the right motor depends on your application - whether for home, industrial, or specialized use!
-400x300.jpeg)
-400x300.jpeg)
