Introduction
When constructing or renovating a private home, selecting the appropriate heating system is crucial. The choice directly influences the living conditions, energy efficiency, and overall comfort of the household. Electric heating systems have gained popularity due to their versatility and the increasing demand for sustainable and intelligent home solutions. This guide explores the different types of electric heating systems-water-based, air-based, and underfloor heating-along with their benefits, drawbacks, and strategies to create an economical heating setup for your home.
Types of Electric Heating Systems
Electric heating systems for private homes can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Water-Based Systems
- Air-Based Systems
- Underfloor Heating
Each type offers unique advantages and suits different household needs and architectural setups.
1. Water-Based Electric Heating Systems
Overview
Water-based electric heating systems utilize an electric boiler to heat water, which is then circulated through radiators or baseboard heaters to warm the home.
Advantages
- Stability: Provides consistent and stable heating throughout the home.
- Thermal Inertia: Capable of maintaining heat even after the boiler is turned off, ensuring prolonged warmth.
- Quiet Operation: Water-based systems operate silently, as the water acts as a thermal buffer.
- Ease of Maintenance: Pipes are relatively easy to replace or repair if damaged.
Disadvantages
- Complex Installation: Requires a network of radiators and pipes, leading to higher initial installation costs and time.
- Slow Temperature Adjustment: Due to thermal inertia, adjusting the temperature quickly is challenging.
- Risk of Pipe Damage: In cold climates, freezing can cause pipes to burst if the heating is turned off.
- Extensive Repairs: Major repairs may necessitate draining the system and complete shutdown.
2. Air-Based Electric Heating Systems
Air-based heating systems distribute warm air throughout the home using various types of heaters and fans.
Types of Air-Based Systems
- Convectors: Utilize natural air circulation to distribute heat.
- Infrared Heaters: Emit infrared radiation to directly warm objects and people in a room.
- Heat Vents and Fans: Use forced air to quickly heat spaces.
Advantages
- Simple Installation: Easier and faster to install compared to water-based systems.
- Quick Heating: Can rapidly increase room temperature, providing immediate comfort.
- Silent Operation: Most air-based heaters operate quietly, enhancing comfort.
- Portability: Many units are lightweight and can be moved between rooms as needed.
Disadvantages
- Uneven Heating: May lead to uneven temperature distribution, with some areas remaining cooler.
- Noise Levels: While generally quiet, some units like heat vents may produce noticeable noise.
- Energy Consumption: Higher energy usage can lead to increased electricity bills.
- Air Drying: Can reduce indoor humidity levels, leading to dry air and potential discomfort.
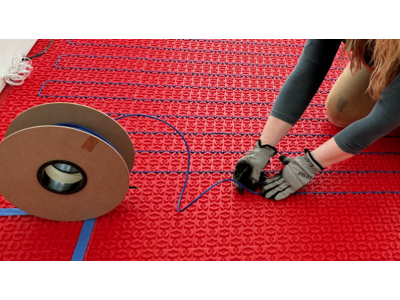
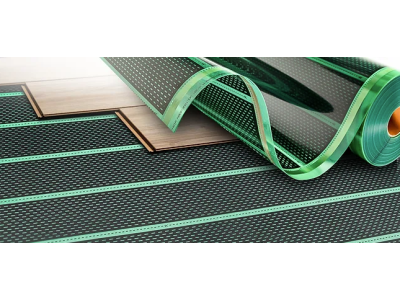
3. Underfloor Electric Heating
Underfloor heating systems provide radiant heat from the floor upwards, ensuring even temperature distribution.
Advantages
- Uniform Heating: Delivers consistent warmth across the entire floor surface.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Eliminates the need for visible radiators, maintaining a clean interior design.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower operating temperatures can result in energy savings.
- Comfort: Provides a comfortable and cozy feel underfoot, especially beneficial in colder climates.
Disadvantages
- High Installation Costs: Installation can be expensive, especially in existing homes requiring floor removal.
- Slow Response Time: Takes longer to heat up and cool down compared to other systems.
- Limited Flexibility: Once installed, it’s difficult to adjust or relocate.
- Electrical Load: Requires sufficient electrical capacity, which might necessitate upgrades to the home’s electrical system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Heating Systems
Advantages
Ease of Installation:
- Electric heating systems are generally easier and quicker to install compared to traditional fuel-based systems. This simplicity can reduce initial setup costs and time.
Flexibility:
- Electric heaters come in various forms, allowing homeowners to choose the most suitable option for each room or area. Portable units provide additional flexibility.
Environmental Friendliness:
- Electric heating produces no direct emissions, contributing to a cleaner indoor environment. When powered by renewable energy sources, it can be a highly sustainable option.
Safety:
- Electric systems eliminate risks associated with fuel storage, such as gas leaks or fires, enhancing overall household safety.
Low Maintenance:
- Electric heating systems typically require less maintenance than their fuel-based counterparts, reducing ongoing maintenance costs and efforts.
Disadvantages
High Energy Consumption:
- Electric heating can lead to higher electricity bills, especially in regions with cold climates requiring extensive heating.
Dependency on Electricity:
- In the event of power outages, electric heating systems become inoperative, potentially leaving the home cold.
Installation Costs for Complex Systems:
- While simpler systems are cost-effective, installing complex setups like water-based heating with extensive piping can be expensive.
Heat Distribution Issues:
- Some electric heating methods, particularly air-based systems, may result in uneven heating, creating cold spots within the home.
Strategies for Creating an Economical Electric Heating System
Implementing cost-efficient strategies can significantly reduce the financial burden of electric heating while maintaining comfort and efficiency.
1. Optimize Control Settings
Thermostat Configuration: Properly setting thermostats can prevent excessive energy use. Programmable or smart thermostats allow precise control over heating schedules and temperature settings.
Zoning: Dividing the home into different heating zones ensures that only occupied areas are heated, reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
2. Enhance Home Insulation
Quality Insulation: Investing in high-quality insulation materials can minimize heat loss, ensuring that the heating system operates more efficiently.
Sealing Leaks: Identifying and sealing gaps around windows, doors, and other entry points prevents warm air from escaping and cold air from entering.
3. Utilize Time-of-Use Electricity Tariffs
- Off-Peak Heating: Taking advantage of lower electricity rates during off-peak hours can lead to significant savings. Scheduling heating systems to operate primarily during these times reduces overall costs.
4. Implement Energy-Efficient Heating Solutions
Energy-Efficient Devices: Choosing heating systems with high energy efficiency ratings ensures optimal performance with lower energy consumption.
Smart Controls: Integrating smart home controls can automate heating adjustments based on occupancy and usage patterns, enhancing energy savings.
5. Regular Maintenance and Upgrades
System Maintenance: Regularly maintaining heating systems ensures they operate efficiently, preventing energy wastage due to malfunctions or inefficiencies.
Upgrade Components: Replacing outdated components with newer, more efficient models can enhance the overall performance and reduce energy consumption.
6. Incorporate Renewable Energy Sources
Solar Panels: Integrating solar panels can offset electricity usage, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering heating costs.
Heat Pumps: Utilizing electric heat pumps, which are more energy-efficient than traditional electric heaters, can provide substantial energy savings.
Conclusion
Electric heating systems offer versatile and efficient solutions for private homes, accommodating various preferences and architectural designs. Whether opting for water-based systems, air-based systems, or underfloor heating, understanding the unique advantages and disadvantages of each type is essential for making an informed decision. By implementing cost-saving strategies such as optimizing control settings, enhancing insulation, and utilizing energy-efficient devices, homeowners can achieve a comfortable living environment while minimizing energy expenses.
Key Takeaways:
Understand Heating Types: Familiarize yourself with the different electric heating options-water-based, air-based, and underfloor-to choose the most suitable for your home.
Focus on Efficiency: Implement strategies like proper thermostat settings, zoning, and enhancing home insulation to maximize energy efficiency.
Leverage Smart Technologies: Utilize smart thermostats and home automation to control heating systems more effectively and reduce energy consumption.
Prioritize Safety: Ensure that all heating installations comply with safety standards to prevent hazards and ensure reliable operation.
Regular Maintenance: Keep heating systems well-maintained to sustain performance and prevent energy wastage.
Consider Renewable Integration: Explore integrating renewable energy sources to offset heating costs and promote sustainability.
Evaluate Costs vs. Benefits: Balance the initial installation costs with long-term energy savings to make economically sound decisions.
Seek Professional Advice: Consult with heating system professionals to design and implement the most effective and efficient heating solution for your home.
Stay Informed: Keep up with advancements in heating technologies to continuously improve and upgrade your system for optimal performance.
Adapt to Seasonal Changes: Adjust heating settings and strategies based on seasonal variations to maintain comfort and efficiency year-round.
For expert assistance in designing and implementing electric heating systems tailored to your private home’s specific needs, visit safsale.com. Our specialists are ready to help you create a reliable, efficient, and comfortable living environment.
Important Notice on Standards
All referenced documents and standards in this guide are provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as official publications. For authoritative guidelines and legal requirements, always consult the official standards organizations or regulatory bodies.