Living in a Smart Home has transitioned from a futuristic concept to a practical reality for many. With advancements in technology, smart home systems offer unparalleled convenience, security, and efficiency, making everyday life simpler and more comfortable. This guide delves into the capabilities of smart home systems, the various methods of their implementation, remote technologies that enhance their functionality, and practical tips for setting up your own smart home. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or a homeowner looking to upgrade your living space, understanding these elements will help you make informed decisions to optimize your home's intelligence and automation.
What is a Smart Home?
A Smart Home refers to a residence equipped with a network of interconnected devices that communicate with each other to automate and enhance various household functions. These systems integrate a wide range of technologies, from security and lighting to climate control and entertainment, enabling centralized management and control through smartphones, tablets, or specialized controllers.
Key Components of a Smart Home:
- Smart Devices: Includes appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and lighting systems that can be controlled remotely.
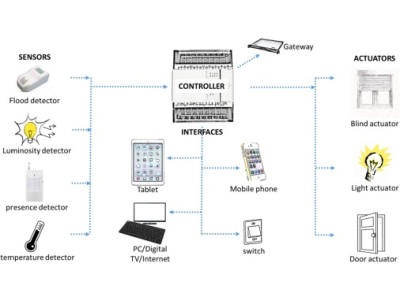
- Sensors: Detect changes in the environment, such as motion, temperature, or light levels, and trigger automated responses.
- Controllers: Central hubs or gateways that manage and coordinate the smart devices within the home.
- Connectivity: Utilizes wireless protocols like Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or Z-Wave to facilitate communication between devices.
- User Interface: Interfaces such as smartphone apps, voice assistants (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant), or dedicated touch panels for controlling and monitoring the system.
Capabilities of Smart Home Systems
Smart home systems offer a multitude of functionalities designed to enhance comfort, security, and energy efficiency. Below are some of the primary capabilities:
1. Lighting Control
- Automated Lighting: Smart lights can be programmed to turn on or off based on schedules, occupancy, or ambient light levels.
- Remote Control: Adjust lighting settings from anywhere using a smartphone or voice commands.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimize energy usage by dimming lights when full brightness is unnecessary or turning them off when rooms are unoccupied.
2. Climate Control
- Smart Thermostats: Automatically adjust temperature settings based on user preferences, occupancy, and external weather conditions.
- Zoned Heating and Cooling: Control different areas of the home independently to enhance comfort and reduce energy consumption.
- Integration with Weather Forecasts: Preemptively adjust climate settings in response to upcoming weather changes.
3. Security and Surveillance
- Smart Locks: Enable remote locking and unlocking of doors, and provide access logs for enhanced security.
- Security Cameras: Monitor your property in real-time, receive alerts for suspicious activities, and store footage for future reference.
- Alarm Systems: Integrated alarms that can be triggered remotely or automatically in response to detected threats.
4. Entertainment Systems
- Smart TVs and Speakers: Stream content, control volume, and manage playback using voice commands or mobile devices.
- Multi-Room Audio: Synchronize music playback across different rooms for a cohesive entertainment experience.
5. Energy Management
- Smart Plugs and Outlets: Monitor and control the power usage of connected devices, helping to reduce energy waste.
- Solar Panel Integration: Manage and optimize the use of renewable energy sources within the home.
6. Home Automation
- Routine Scheduling: Automate daily tasks such as turning on lights at sunset or adjusting the thermostat before arriving home.
- Scene Setting: Create custom scenes that adjust multiple devices simultaneously for specific activities (e.g., "Movie Night" dims the lights and turns on the TV).
Implementation Methods for Smart Home Systems
Implementing a smart home system can be approached in various ways, depending on your budget, technical expertise, and specific needs. Here are the primary methods of realization:
1. DIY (Do-It-Yourself) Installation
Overview:
- Suitable for tech-savvy individuals who prefer hands-on control over their smart home setup.
- Involves purchasing individual smart devices and integrating them using compatible platforms or hubs.
Steps:
- Assess Needs: Determine which aspects of your home you want to automate (e.g., lighting, security, climate control).
- Choose a Hub: Select a central hub or platform (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Home, Apple HomeKit) to coordinate your devices.
- Purchase Devices: Buy compatible smart devices that align with your chosen hub.
- Install and Configure: Set up each device according to the manufacturer's instructions and integrate them with your hub.
- Create Routines: Program automated routines and scenes to enhance functionality.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective compared to professional installation.
- Flexibility to customize the system according to personal preferences.
Considerations:
- Requires a certain level of technical knowledge.
- May involve troubleshooting compatibility issues between different devices.
2. Professional Installation
Overview:
- Ideal for those who prefer expert assistance or have complex smart home requirements.
- Involves hiring certified professionals to design, install, and configure the smart home system.
Steps:
- Consultation: Meet with a smart home specialist to discuss your needs and preferences.
- System Design: Work with the installer to design a tailored smart home setup that integrates various devices seamlessly.
- Installation: Allow professionals to install and configure the hardware and software components.
- Training: Receive guidance on using and managing your new smart home system.
- Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance.
Advantages:
- Expert knowledge ensures a reliable and efficient setup.
- Saves time and reduces the likelihood of installation errors.
- Comprehensive support and warranty services.
Considerations:
- Higher initial cost compared to DIY installation.
- Limited flexibility if you wish to add new devices in the future without additional professional assistance.
3. Hybrid Approach
Overview:
- Combines DIY and professional installation methods.
- Allows for partial professional setup while retaining the flexibility to add and manage some devices independently.
Steps:
- Professional Core Setup: Hire professionals to install the central hub, main security systems, and critical devices.
- DIY Expansion: Add additional smart devices and customize settings on your own using the installed hub.
- Ongoing Management: Maintain and expand the system as needed, leveraging both professional support and personal initiative.
Advantages:
- Balances expert installation with personal customization.
- Cost-effective while still benefiting from professional setup for essential components.
Considerations:
- Requires coordination between professional services and personal setup.
- May still involve some technical challenges when integrating new DIY components.
Remote Technologies in Smart Homes
Remote Technologies play a pivotal role in enhancing the functionality and convenience of smart home systems. They enable homeowners to control and monitor their home’s devices from virtually anywhere, offering unprecedented flexibility and peace of mind.
1. Wi-Fi Connectivity
- Functionality: Most smart devices connect to the home’s Wi-Fi network, allowing remote access via smartphone apps or web interfaces.
- Advantages: High-speed data transfer, widespread availability, and ease of integration with other smart devices.
- Use Cases: Controlling lighting, adjusting thermostats, viewing security camera feeds, and managing entertainment systems remotely.
2. Bluetooth
- Functionality: Enables short-range communication between devices, typically within 30 feet.
- Advantages: Low power consumption and easy setup for nearby device interactions.
- Use Cases: Connecting speakers, headphones, and smart locks for quick and localized control.
3. Zigbee and Z-Wave
- Functionality: Specialized wireless protocols designed for smart home devices, offering reliable and secure communication.
- Advantages: Low power usage, mesh networking capabilities (allowing devices to relay signals), and reduced interference.
- Use Cases: Integrating a wide range of smart home devices, including lights, sensors, and security systems, for seamless and interconnected control.
4. Cellular Networks (3G, 4G, 5G)
- Functionality: Provides connectivity for smart devices outside the range of traditional home networks, utilizing mobile data networks.
- Advantages: Extensive coverage, reliability, and ability to connect devices remotely without relying on the home’s internet connection.
- Use Cases: Enabling remote access and control for outdoor cameras, security systems, and home automation devices even when homeowners are away.
5. Infrared (IR) Remote Control
- Functionality: Uses infrared signals to communicate between devices and remote controllers.
- Advantages: Simple and effective for line-of-sight control.
- Use Cases: Controlling entertainment systems like TVs and audio receivers through dedicated remote apps or physical remotes.
6. Voice Assistants and AI Integration
- Functionality: Integrates with voice-activated assistants (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, Apple Siri) to allow hands-free control.
- Advantages: Enhances user convenience and accessibility, enabling control through natural language commands.
- Use Cases: Managing lighting, climate control, security systems, and entertainment devices using voice commands.
Practical Tips for Setting Up a Smart Home System
1. Plan Your Smart Home Layout
- Assess Needs: Identify which areas of your home would benefit most from automation (e.g., security, lighting, climate control).
- Prioritize Devices: Start with essential devices that offer the most significant benefits, such as smart locks, thermostats, and security cameras.
- Consider Future Expansion: Choose a system that allows easy addition of new devices as your needs evolve.
2. Ensure Compatibility
- Unified Platforms: Opt for devices that are compatible with a single smart home platform or hub to ensure seamless integration.
- Manufacturer Consistency: Using devices from the same manufacturer can reduce compatibility issues and simplify setup.
3. Secure Your Network
- Strong Passwords: Use robust, unique passwords for your Wi-Fi network and smart home accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Updates: Keep all devices and software up to date with the latest security patches and firmware updates.
- Network Segmentation: Consider setting up a separate network for your smart devices to enhance security and reduce potential vulnerabilities.
4. Optimize Device Placement
- Strategic Placement: Position devices where they can function optimally, such as placing motion sensors in high-traffic areas or ensuring security cameras have unobstructed views.
- Avoid Interference: Keep devices away from sources of interference, such as thick walls or electronic appliances, to maintain reliable connectivity.
5. Utilize Automation and Routines
- Create Routines: Set up automated routines that trigger multiple actions based on specific conditions, like turning off all lights and locking doors when leaving the house.
- Leverage Sensors: Use sensors to automate responses, such as adjusting the thermostat based on occupancy or time of day.
6. Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
- Routine Checks: Regularly inspect and test your smart home devices to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Monitor Usage: Keep an eye on device performance and connectivity to address any issues promptly.
7. Educate All Users
- User Training: Ensure that all household members understand how to use and manage the smart home system effectively.
- Access Control: Assign appropriate access levels to different users to maintain security and prevent accidental changes to settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the Benefits of Implementing a Smart Home System?
Answer: Smart home systems offer numerous benefits, including enhanced security through surveillance and smart locks, increased energy efficiency with automated lighting and climate control, improved convenience through remote and voice-activated controls, and the ability to customize and automate daily tasks to suit individual lifestyles.
2. Can I Start with a Smart Home System and Expand Over Time?
Answer: Absolutely. Many smart home systems are designed to be modular, allowing you to start with a few essential devices and expand the system as your needs and budget allow. This approach helps manage costs and ensures that the system grows with your requirements.
3. How Secure Are Smart Home Systems?
Answer: When properly configured, smart home systems can be highly secure. It is crucial to use strong, unique passwords, keep all devices and software updated, and implement network security measures such as firewalls and network segmentation. Choosing reputable manufacturers and secure communication protocols also enhances system security.
4. Do Smart Home Systems Work Without Internet Connectivity?
Answer: Some smart home systems can operate without a constant internet connection, relying on local network communication between devices. However, remote access and certain advanced features typically require internet connectivity. It is advisable to have a stable internet connection to fully utilize all functionalities of a smart home system.
5. What Should I Consider When Choosing a Smart Home Hub?
Answer: When selecting a smart home hub, consider compatibility with your existing or planned devices, ease of use, supported communication protocols (e.g., Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave), integration with voice assistants, and the availability of automation features. Additionally, evaluate the hub’s reliability and the manufacturer's reputation for updates and support.
Final Thoughts
Smart Home Systems represent the future of residential and commercial living, offering unparalleled convenience, security, and efficiency. By understanding the capabilities, various implementation methods, and the role of remote technologies, you can create a smart home environment that caters to your unique needs and preferences. Whether you choose a DIY approach, professional installation, or a hybrid method, careful planning and informed decision-making are essential to achieving a seamless and effective smart home setup.
Key Takeaways:
Assess Your Needs: Identify the areas of your home that will benefit most from automation and prioritize those for initial setup.
Choose Compatible Devices: Select devices that work well together and integrate seamlessly with your chosen smart home hub or platform.
Secure Your Network: Implement strong security measures to protect your smart home system from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Plan for Future Expansion: Opt for scalable systems that allow you to add new devices and functionalities as your needs evolve.
Utilize Automation: Leverage routines and sensor-based automation to enhance efficiency and convenience in your daily life.
Regular Maintenance: Keep your system updated and conduct routine checks to ensure all components are functioning optimally.
Educate Household Members: Ensure everyone in your home understands how to use and manage the smart home system effectively.
Consider Professional Help: For complex installations or high-security requirements, seek assistance from certified smart home professionals to ensure a reliable and secure setup.
Explore Remote Technologies: Utilize remote control and monitoring technologies to manage your smart home from anywhere, enhancing flexibility and peace of mind.
Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest advancements in smart home technology to continuously improve and upgrade your system.
For expert assistance in designing and implementing smart home systems, ensuring compliance with relevant standards, or accessing comprehensive project documentation, visit safsale.com. Our specialists are ready to help you create a reliable, compliant, and efficient smart home tailored to your specific needs.
Important Notice on Standards
All referenced documents and standards in this guide are provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as official publications. For authoritative guidelines and legal requirements, always consult the official standards organizations or regulatory bodies.