AUTOMATIC FIRE ALARM SYSTEMS
Installation, Types, and Modern Integration
Automatic fire alarm systems (AFAS) are vital for early fire detection and notification. They consist of advanced tech designed to spot fires at their earliest stages and alert building occupants and emergency responders.
In today’s world, where safety takes center stage, having a professionally designed and installed fire alarm system isn’t just a perk-it’s a necessity.
PRIMARY GOALS OF AFAS
The main purpose of a fire alarm system is simple:
- Early fire detection to save lives.
- Efficient alarm signaling to minimize property damage.
Statistics back this up: buildings equipped with modern fire alarm systems are significantly safer when fires occur.
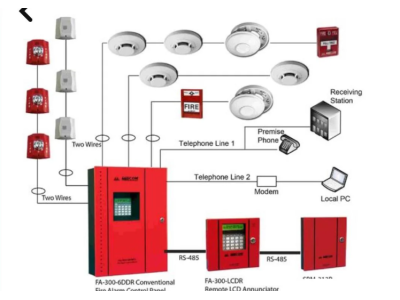
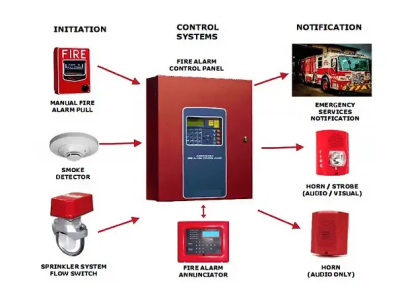
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
Control Panels
The control panel is the brain of the system.
- It processes data from sensors and manages alarm notifications.
- Modern panels feature microprocessors, reducing false alarms.
Control panels range from small setups for homes to industrial-grade systems for large facilities. The size and type depend on the property’s layout and fire risk.
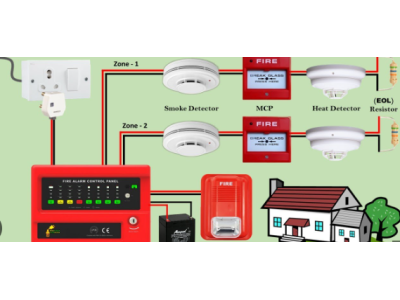
Detectors
Fire detectors identify signs of fire. Common types include:
- Smoke detectors: Perfect for most settings. These detect smoke particles and often include self-diagnostic features.
- Heat detectors: Ideal for areas with dust or steam, reducing false alarms.
- Flame detectors: Effective in high-risk industrial areas.
- Manual call points: Allow users to trigger alarms directly.
Notification Systems
Fire alarm systems include evacuation tools like:
- Audible and visual alarms: Sirens and flashing lights.
- Directional signs: Highlight evacuation routes with illuminated "EXIT" signs.
- Voice alarms: Provide clear evacuation instructions.
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
Planning the System
Fire alarm design starts with an on-site survey to:
- Assess fire risk for each area.
- Map out device locations based on floor plans and ventilation.
The design process includes structural diagrams and sensor type selection while meeting regulatory codes.
Installation
Professional technicians handle system installation, focusing on:
- Durable wiring capable of withstanding fire conditions.
- Proper sensor placement for maximum coverage.
- Easy access for future maintenance.
Maintenance and Inspections
Regular checkups ensure system reliability:
- Monthly: Visual inspections and basic function tests.
- Quarterly: Electrical testing and power supply verification.
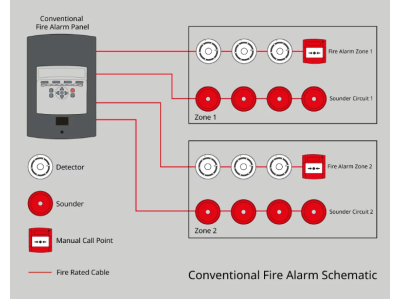
TYPES OF FIRE ALARM SYSTEMS
- Threshold Systems
- Best for small spaces with moderate fire risks.
- Cost-effective and simple but less precise.
- Addressable Systems
- Each detector is uniquely identified.
- Provides detailed system status and reduces downtime.
- Addressable-Analog Systems
- Advanced systems where the control panel analyzes sensor data.
- Highly accurate, reducing false alarms and pinpointing fire origins.
NOTIFICATION AND FIRE SUPPRESSION
When a fire is detected, the system activates:
- Evacuation alerts: Using light, sound, or voice systems.
- Access control overrides: Unlocking doors and halting elevators.
- Fire suppression systems: Deploying gas, water, or foam agents based on the property’s needs.
MODERN ADVANCEMENTS IN FIRE ALARMS
Integrated Safety Systems
Modern fire alarms link with:
- HVAC systems for smoke control.
- Surveillance cameras for incident recording.
- Access controls for safe evacuations.
Smart Technology
AI-driven fire alarms allow remote monitoring and reduce false alarms.
CONCLUSION
Automatic fire alarm systems are crucial for protecting lives and property. From simple setups to integrated smart systems, they’re essential for modern safety standards.
Looking for reliable fire safety solutions? Check out safsale.com for the best options tailored to your needs!
-400x300.png)