Understanding Diodes: How They Work and Where They’re Used
1️⃣ What is a Diode?
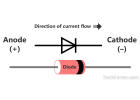
A diode is an electronic component that allows current to flow in only one direction. It consists of two terminals:
✔ Anode (+) - Positive side
✔ Cathode (-) - Negative side
The main function of a diode is to block current flow in the reverse direction, making it essential in rectifiers, voltage regulators, and signal processing circuits.
2️⃣ Types of Diodes
- Rectifier Diodes - Used in power supplies
- Schottky Diodes - Low voltage drop, fast switching
- Zener Diodes - Voltage regulation
- Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) - Emit light when forward-biased
- Photodiodes - Convert light into electricity
Each type of diode is designed for a specific function, but they all follow the same basic principle of directing current flow.
3️⃣ How a Diode Works: Forward and Reverse Bias
✔ Forward Bias (Conducting Mode)
When the anode is connected to the positive voltage, and the cathode is connected to the negative, the diode allows current to flow.
Key Characteristics:
✔ The diode "opens" and conducts electricity
✔ Voltage drop occurs (typically 0.7V for silicon diodes, 0.3V for Schottky diodes)
✔ Used in rectifiers, power circuits, and logic gates
✔ Reverse Bias (Blocking Mode)
When the anode is connected to negative and the cathode to positive, the diode blocks current flow.
Key Characteristics:
✔ The diode "closes" and stops current
✔ A small leakage current may exist, but it's negligible
✔ If the reverse voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage, the diode can fail or conduct uncontrollably
4️⃣ Diode Voltage-Current Characteristics (V-I Curve)
The V-I characteristic curve (Voltage vs. Current) shows how a diode behaves in different conditions.
Threshold Voltage (U_open) - The voltage needed for conduction (0.7V for silicon, 0.3V for Schottky)
Breakdown Voltage (U_break) - The voltage at which a diode starts conducting in reverse (dangerous unless designed for it, like Zener diodes)
Key Takeaways from V-I Curve:
✔ A diode does not conduct until its threshold voltage is reached
✔ In reverse bias, current remains near zero until breakdown occurs
✔ Once conducting, the diode maintains nearly constant voltage while allowing current flow
5️⃣ Real-World Diode Circuit Example
Automatic Battery Backup Circuit
Problem:
You want to power a radio or small device using batteries, but also connect a power adapter when available.
Solution:
Using a diode in series with the battery prevents the adapter from charging the battery while ensuring an automatic switch-over.
How It Works:
✔ When the adapter is plugged in, the diode blocks the battery and prevents discharge
✔ When the adapter is disconnected, the battery automatically powers the device
This simple circuit ensures seamless switching between power sources without damaging the battery or the device.
6️⃣ Practical Applications of Diodes
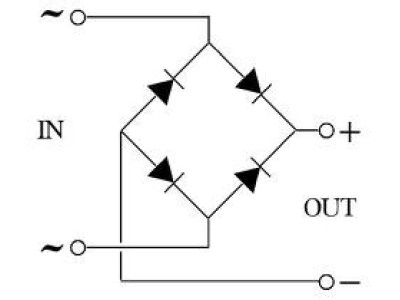
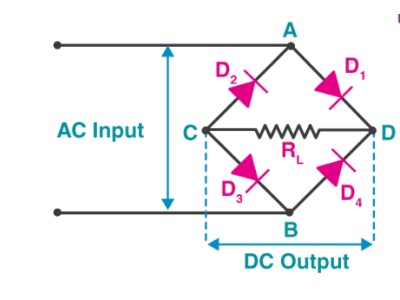
✔ Rectification: Converts AC to DC in power supplies
✔ Voltage Clamping: Protects circuits from voltage spikes
✔ Logic Gates: Used in digital circuits for switching
✔ LED Lighting: Emits light when conducting
✔ Solar Panels: Prevents reverse current flow
7️⃣ Conclusion: Key Takeaways
✔ A diode is a one-way electrical gate
✔ Forward bias allows current flow; reverse bias blocks it
✔ Diodes have a small voltage drop (~0.7V for silicon, ~0.3V for Schottky)
✔ Breakdown voltage must be avoided unless using Zener diodes
✔ They are essential in rectifiers, voltage regulators, and signal processing
Understanding diodes helps you build circuits efficiently, whether in power supplies, signal processing, or voltage protection. ?