IP CAMERAS WITH PoE POWER
CLASSIFICATION AND STANDARDS
EQUIPMENT
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology enabling IP cameras and related devices to receive power over the same Ethernet cable (UTP category 5 or higher) used for data transmission.
This method provides a constant voltage of 48 volts with a power range of 15.4 to 25.5 watts, depending on the standard, and a current of 400 mA. Using PoE does not compromise video quality or introduce interference because:
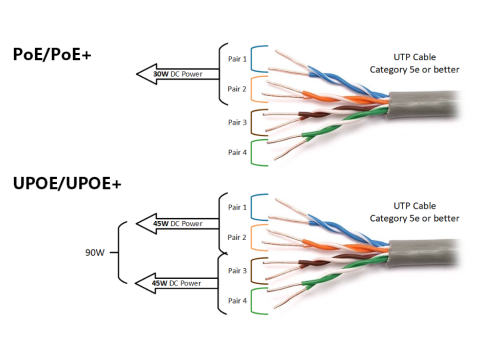
- Separate Power Lines: Electricity is transmitted through pairs of wires not used for data. Ethernet’s 100Base-TX standard reserves only two of the four pairs in a UTP cable for data.
- High-Frequency Transformers: Power is isolated from the data flow using transformers, ensuring the video signal remains unaffected.
POWER SUPPLY TO IP CAMERAS
The PoE power supply connects to the RJ-45 port of an IP camera only if the camera supports PoE. If you accidentally plug a non-PoE camera into a powered port, the camera will remain safe and operational.
Power Delivery Steps:
Compatibility Check:
The PoE adapter tests the device's resistance using a low test voltage (up to 10 volts). Cameras with resistance between 19-25.3 kOhms are recognized as PoE-compatible.Power Classification:
Devices are categorized into four power classes based on their energy needs. If a device exceeds allowable power limits, it is disconnected. For example:- Class 0: Up to 4.5 W
- Class 1: 3.84-6.49 W
- Class 2: 6.49-12.95 W
- Class 3: Up to 15.4 W
Full Power Delivery:
After classification, the system gradually supplies full power (48 volts). The PoE adapter monitors the current draw to prevent overloading.
PoE STANDARDS
Widely adopted standards include:
- IEEE 802.3af: Supplies 48V at up to 15.4 W, using spare wire pairs.
- IEEE 802.3at (PoE+): Supplies up to 25.5 W by leveraging all wire pairs, including those used for data transmission.
Power Transmission Methods:
- Type A: Supplies power via pairs that also carry data (phantom power).
- Type B: Uses unused wire pairs for power transmission.
Most IP cameras are compatible with either method and can accept reversed polarity without issue.
PoE EQUIPMENT
PoE devices fall into two categories:
- PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment): Devices like PoE switches or injectors supplying power.
- PD (Powered Devices): Devices like IP cameras receiving power.
For robust systems, select PoE switches based on:
- Total port power.
- Maximum power per port.
Most PoE switches power only a portion of their ports. If choosing an injector, prioritize models with galvanic isolation and protection against surges.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Benefits of PoE:
- Simplified Setup: One cable handles power and data, saving on materials and installation costs.
- Cost-Effective Upgrades: Existing infrastructure can be reused for PoE-enabled systems.
- Increased Safety: Eliminates reliance on external power sources, enhancing security.
- Remote Reboot Capability: Devices can be restarted remotely, avoiding physical maintenance trips.
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to traditional systems.
- Increased power demands may require upgrading electrical infrastructure.
PoE is ideal for medium to small-scale indoor surveillance systems. However, outdoor setups with additional components (e.g., IR lighting, heating elements) often exceed PoE's power limits, requiring supplementary power sources