Surveillance Camera Components
The functionality of a surveillance camera depends on its core components, which include:
- Lens
- Image Sensor (Matrix)
- Video Signal Processing Unit
- Lens Control Mechanism*
- Infrared (IR) Filter*
(*Not included in all models.)
1. Lens
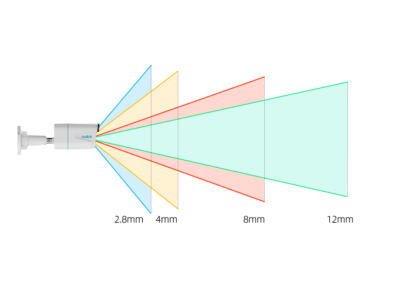
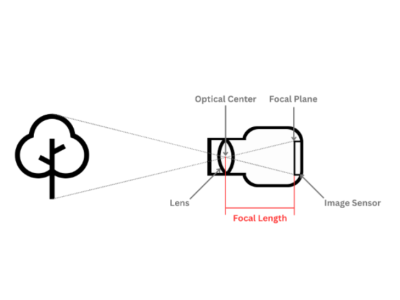
The lens focuses and forms an image on the camera's matrix. Lenses come in various types:
- Basic Lenses: Fixed-focus lenses found in simpler models.
- Advanced Lenses: Include manual or automatic adjustments for:
- Aperture (Diaphragm): Controls the amount of light reaching the matrix.
- Focal Length: Determines the field of view and zoom capabilities.
The quality of the lens is crucial for achieving sharp, detailed images, often accounting for a significant portion of the total camera cost in high-end models.
2. Image Sensor (Matrix)
The matrix converts optical images into electrical signals. Two primary types of matrices are:
CCD (Charge-Coupled Device):
- Produces analog signals.
- Offers high light sensitivity and low noise.
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor):
- Produces digital signals.
- Typically less sensitive to light and noisier than CCD.
Matrix Key Characteristics:
- Pixel Count: Affects resolution; more pixels = higher resolution.
- Format Size: Determines diagonal size in inches (e.g., 1/4", 1/3", 1/2"). Larger formats improve light sensitivity.
3. Video Signal Processing Unit
This unit performs multiple critical tasks, including:
- Managing readout modes.
- Amplifying video signals.
- Controlling operational modes like day/night switching, automatic aperture adjustment, backlight compensation, and electronic shutters.
In IP cameras, this processing unit functions as a miniature computer, featuring:
- Processors
- Memory
- Compression Modules
4. Lens Control Mechanism*
Cameras with advanced lenses often include control systems for automatic aperture adjustments or zoom functions. Basic models may lack this feature.
5. Infrared (IR) Filter*
Found in cameras with day/night functionality, the IR filter enhances performance in low-light or nighttime conditions by:
- Removing color distortions in daylight.
- Switching to monochrome mode for higher sensitivity at night.
Additional Insights
For most consumers, understanding these components helps make informed decisions when choosing cameras. This knowledge focuses on functionality and performance, avoiding overly technical details.
Whether you’re setting up a home or business surveillance system, knowing how cameras work ensures you choose the right model to meet your security needs.