How a Bridge Rectifier Works: Circuit, Function & Applications
1️⃣ What Is a Bridge Rectifier?
A bridge rectifier is a circuit composed of four diodes that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It is commonly used in power supplies to provide stable DC voltage from an AC source.
🔹 Converts AC to DC (full-wave rectification)
🔹 Utilizes both halves of the AC cycle
🔹 Provides a smoother and more efficient output than half-wave rectifiers
A standard bridge rectifier circuit consists of:
✔ Four diodes (arranged in a bridge configuration)
✔ AC input terminals
✔ DC output terminals
2️⃣ Bridge Rectifier Circuit Diagram
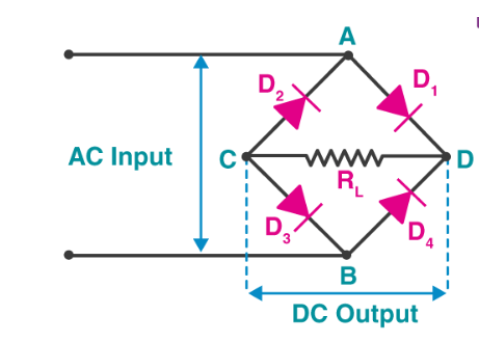
Basic Bridge Rectifier (Single-Phase)
The standard single-phase bridge rectifier circuit is shown below:
🛠 Components:
✔ Diodes (D1, D2, D3, D4) - Conduct current in specific directions
✔ AC input (A, B terminals) - Connected to a transformer or AC source
✔ DC output (C, D terminals) - Provides rectified voltage
🔹 Working Principle:
1️⃣ Positive Half-Cycle:
- D1 & D3 conduct (allowing current flow)
- D2 & D4 block current
- Current flows from A to B, generating a positive output
2️⃣ Negative Half-Cycle:
- D2 & D4 conduct
- D1 & D3 block current
- Current still flows in the same direction on the output
📌 Result: The rectifier converts AC into pulsating DC, maintaining a consistent polarity.
3️⃣ Three-Phase Bridge Rectifier
For higher efficiency, a three-phase bridge rectifier is used. This is commonly found in industrial power supplies and alternators.
🛠 Key Features:
✔ Uses six diodes instead of four
✔ Provides lower ripple voltage
✔ More efficient for high-power applications
🔹 Working Principle:
Each phase contributes power in a 120-degree shift, reducing voltage ripple and improving efficiency.
4️⃣ Bridge Rectifier with a Capacitor Filter
Since rectifiers produce pulsating DC, a capacitor (C) is often added to smooth the output.
🔹 How It Works:
✔ Capacitor Charges during peaks
✔ Releases Stored Energy during voltage drops
✔ Reduces Ripple, making DC more stable
🔹 Applications:
✔ Power Adapters (e.g., phone chargers)
✔ DC Power Supplies
✔ Battery Charging Circuits
5️⃣ Real-World Applications of Bridge Rectifiers
✔ Power Supply Circuits - Converts AC mains to DC for electronics
✔ Battery Chargers - Converts AC for efficient charging
✔ Motor Drive Circuits - Provides DC power for industrial motors
✔ Welding Equipment - Delivers stable DC current
6️⃣ Key Takeaways
✔ A bridge rectifier converts AC to DC using four (or six) diodes
✔ It is more efficient than a half-wave rectifier
✔ A capacitor filter smooths out the output voltage
✔ Used in power supplies, battery chargers, and industrial applications
A bridge rectifier is an essential AC-DC conversion component, ensuring stable and efficient power delivery for countless electronic applications! 🚀