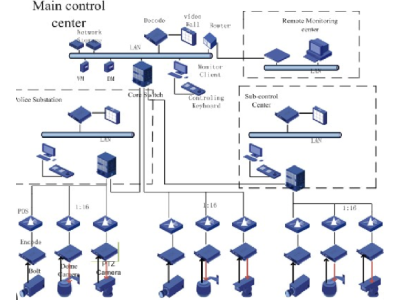
Modern CCTV Systems
Technology and Cameras
The Evolution of Video Surveillance
Today’s video surveillance tech is evolving fast, with key improvements happening in several areas:
- Better image quality for sharper visuals
- Growing use of cloud-based services
- Advanced video analytics tools
- New ways to access systems remotely via the internet
Analog vs. IP Systems
There’s an ongoing rivalry between traditional analog systems and more modern IP (network) cameras. Despite the buzz around digital, analog still holds its ground. One of the big wins for IP cameras was high resolution, but recent advancements have leveled the playing field with technologies like:
- HDCVI
- HDTVI
- AHD
AHD has become especially popular because of its tech perks, delivering megapixel-quality images while keeping things simple and affordable for most surveillance needs. AHD systems also use standard coaxial cables, making upgrades easy without rewiring-a major plus for homes or small businesses with existing analog setups.
Why IP Cameras Shine
IP cameras dominate certain use cases, especially when it comes to remote viewing over the internet. Let’s break down the remote access options:
Remote Access Technology
Internet connectivity is king when it comes to managing modern video surveillance systems. You can now monitor and control cameras using everything from desktop PCs to tablets and smartphones. The two main ways to access footage remotely are:
- Cloud-based services
- Direct connections to local storage devices like DVRs or PCs
Cloud-based systems are gaining traction because they simplify setup-many cameras register automatically with a provider’s server, making configuration a breeze. While this convenience is great, it can limit compatibility with other standalone systems.
That said, most modern DVRs and IP cameras now offer internet connectivity without requiring a static IP address. But remember, some off-brand gear might have issues with certain software or services. Always check for compatibility before buying.
Video Analytics
Video analytics is a hot topic, but outside basic motion detection and signal loss alerts, most advanced features are highly specialized. Here are a few examples:
- Object Left Behind Detection - Useful for spotting suspicious packages in public places
- Object Recognition - From license plate readers to facial recognition
- People Counting - Helps track foot traffic in retail or transit stations
Cutting-Edge Camera Tech
The innovation in surveillance cameras spans a few critical areas:
Sensor Technology: The challenge is balancing higher resolution with better low-light performance. More pixels mean smaller sensor areas, which usually cuts down on sensitivity. Sony tackled this by designing a curved sensor surface, boosting light sensitivity by 1.5x and reducing noise levels for better low-light images.
Features and Options: Modern cameras come with on-screen display (OSD) menus and built-in analytics. OSD lets users fine-tune settings directly. For IP cameras, built-in analytics (like motion detection) reduce the load on central servers and network bandwidth, making systems more efficient. Improved video compression technologies further optimize performance.
Signal Processing: New formats like HDCVI, HDTVI, and AHD enable HD-quality video in analog setups, cutting costs and simplifying installation without compromising image clarity.
In summary, whether you're upgrading an old setup or diving into the latest IP tech, today’s surveillance systems offer flexible, powerful options for every need.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Recent innovations in camera design focus on both hardware and software improvements. Companies are developing superior image sensors and enhancing onboard processing capabilities to deliver:
- Higher Sensitivity: Bigger pixel arrays combined with smarter software boost light capture, making night surveillance much clearer.
- Noise Reduction: Algorithms that clean up video feed without sacrificing sharpness.
Modern signal handling technologies like HDCVI, HDTVI, and AHD allow users to build cost-effective HD systems with analog gear, combining high performance with easy setup. The days of expensive upgrades are gone-these systems let users transform older installations without tearing out cables.