Installing an RCBO (Difavtomat) without Ground: Is It Safe?
Some electrical codes may discourage connecting a Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent (RCBO, often akin to a GFCI plus breaker) in a single-phase system without a dedicated ground. However, many professionals argue that using an RCBO without a ground is still far better than having no protection at all. Below, we’ll explore the reasoning behind this perspective, discussing how RCBOs function, the risks involved, and the practical benefits for electrical safety in the USA.
Note: Specific electrical codes can vary by jurisdiction. Always consult local regulations and, if necessary, a licensed electrician. For extra guidance on electrical safety, check safsale.com, where we share in-depth installation tips and product insights relevant to the USA market.
1. Revisiting the Core Principle of RCBO (GFCI) Protection
A RCBO protects people and equipment by monitoring the incoming current (hot conductor) against the outgoing current (neutral conductor). If there is a difference-known as residual current or leakage current-the device trips and opens the circuit. Typical trip ratings for personal protection range from 30 mA (milliamps) to higher values for different applications.
What Happens to the Missing Current?
The RCBO doesn’t care where the lost current goes. It could flow through a person, a metal chassis, or any unintended pathway to ground. Once this imbalance exceeds the device’s trip threshold, the circuit is disconnected.Human Safety Thresholds
- Currents around 100 mA can be fatal if they pass through the human body for a sufficiently long time.
- A 30 mA trip rating (often called the “gold standard” for shock protection) typically interrupts current fast enough to help prevent serious injury or death.
Trip Times
While exact trip times vary, common industry benchmarks often require an RCBO to operate within:- 300 ms for nominal differential current (In).
- 150 ms for 2 × In.
- 40 ms for 5 × In.
If a leak is significant, the higher multiple of In should trigger a faster disconnect.
This rapid disconnection is crucial. The likelihood of severe injury diminishes significantly if the shock current is interrupted within roughly 100 ms or less.
2. How an RCBO Works Without Ground
When you don’t have a dedicated ground wire:
- An RCBO still measures the current difference between hot and neutral.
- If the metal chassis of an appliance unintentionally becomes energized and a person touches it, the leaking current typically flows through the person’s body to a grounded surface, or possibly through other conductive paths in the environment.
- This imbalance triggers the RCBO to open the circuit, cutting power and protecting the user from prolonged electrocution.
The Potential Risk without Ground
If the chassis becomes live but no one (or nothing) provides a path to ground, the RCBO might not trip until a person contacts the chassis and inadvertently creates a leakage path. That’s still preferable to having no protection, as the RCBO will trip as soon as the leakage occurs through a person, drastically reducing shock time.
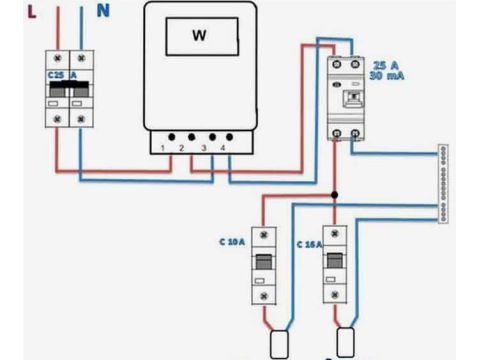
3. Simplified Connection Diagram (No Ground)
- Hot line enters the RCBO on the “in” terminal and leaves on the “out” terminal.
- Neutral line does the same.
- With no separate ground, the appliance chassis is not bonded to a dedicated grounding conductor.
- The RCBO trips if there’s any imbalance between hot and neutral, whether that current escapes through a person or another unintended path.
4. Alternative Wiring Trick (Chassis Tied to Neutral Before RCBO)
Some individuals connect the appliance chassis to the neutral conductor upstream of the RCBO. From a strict code perspective, this might be questionable or disallowed in many regions, but here’s the rationale:
- If the appliance chassis accidentally becomes energized, current immediately flows back to the panel via the neutral (bypassing the RCBO).
- The RCBO detects the missing current from its neutral output and trips quickly.
Potential Hazards
- Short-Circuit Condition: If a hot conductor contacts the neutral in an unintended way, the circuit breaker or the supply fuse may blow, or the RCBO itself might trip.
- Voltage Surges: If multiple phases or supply issues cause abnormal voltages on the neutral, equipment can be damaged (e.g., 240-380 V situations in certain multi-phase or miswired environments).
In general, this wiring is unconventional in the USA and often not recommended by modern electrical codes. It introduces complexities if the neutral fails or is miswired.
5. What If the Neutral Fails or Shorts?
A major concern in older or compromised systems is the possibility of the neutral conductor opening (failing) somewhere upstream:
- No Effective Return Path: The circuit might revert to a situation where the chassis could be live until a person or another path supplies a leakage route.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Lost neutral can lead to dangerously high voltages on certain circuits, damaging electronics.
- RCBO Limitations: While an RCBO can still trip if there’s a leakage current, it won’t prevent all overvoltage events triggered by a missing neutral.
6. Conclusion: Is an RCBO without Ground Worth It?
Even though many codes emphasize installing a proper grounding system, using an RCBO without a dedicated ground is typically safer than having no ground-fault protection at all. The device will still protect against shock by disconnecting power quickly as soon as a leakage current path emerges.
- Yes, it’s safer than zero protection: The risk of a sustained electrocution decreases significantly with an RCBO in place.
- No, it’s not a substitute for proper grounding: The ideal setup includes a dedicated ground conductor so the chassis is never live.
- Always follow local codes: Check your local regulations or consult a licensed electrician to ensure compliance with USA standards.
For more information on RCBO installations, potential hazards, and recommended products for the American market, visit safsale.com. We regularly publish updates on electrical safety, new technologies, and best practices to help you stay compliant and protected.
Key Takeaways
- RCBO (Difavtomat) Function
Combines overcurrent and ground-fault protection in one device. - Leakage Detection
Trips when hot and neutral currents differ, protecting against accidental shocks. - Without Ground
The chassis might stay energized until a person contacts it, but the RCBO still drastically reduces shock duration. - Wiring Alternatives
Tying the chassis to neutral upstream is sometimes practiced but often discouraged by modern codes. - Always Put Safety First
An RCBO without ground isn’t perfect, but it’s superior to no protection. Aim for a fully grounded system whenever possible.
Stay safe, stay informed, and consult local regulations if you’re unsure about installing an RCBO without ground in your single-phase system. Proper precautions can make all the difference in preventing electrical hazards.