Reed switches aren’t just one specific device—they’re more of a broad term covering a range of components designed to control electrical circuits through magnetic influence. Whether you’re dealing with limit switches or contactless types, they all operate on a simple yet effective principle.
What Is a Reed Switch?
At its core, a reed switch is all about switching an electrical circuit on or off. These circuits can be:
- Power circuits
- Low-voltage circuits
- Control circuits
- Signal circuits
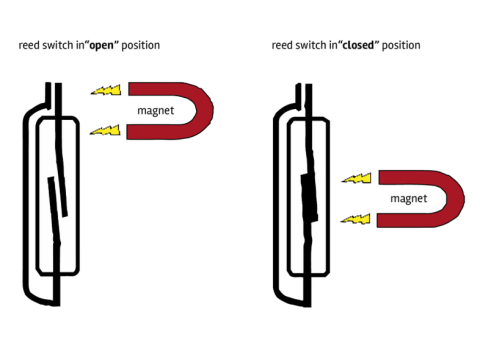
The key component is the reed itself—short for "hermetically sealed contacts." This consists of metal contacts enclosed in a glass tube that reacts to magnetic fields. When exposed to a magnet, these contacts either close or open the circuit.
You might hear people refer to "contactless reed switches." While the activation is indeed contactless (thanks to magnetic fields), the actual contacts inside still physically move to open or close the circuit. This design brings a bunch of advantages:
- Fast response times
- Reliable switching
- Long lifespan
That’s why reed switches are so popular in various sensors and automation systems.
Power Applications and Workarounds
Reed switches aren’t typically used for high-power circuits due to their limited capacity. But there’s an easy fix: pair them with solid-state or electromagnetic relays. The reed handles the control, while the relay manages the heavy lifting. This combo is perfect for things like automated gate systems.
Reed Limit Switches
Limit switches with reed sensors are commonly used to detect the position of moving parts, like doors or gates. The benefits?
- High reliability since there are no mechanical parts that wear out
- Easy adjustment for fine-tuning trigger positions
They can be triggered by an electromagnet (like a solenoid) or, more commonly in limit switches, a simple permanent magnet. The magnet is mounted on the moving part, while the reed switch stays stationary. When the magnet gets close (usually within 0.4 to 2 inches, depending on the model), the circuit reacts.
To boost performance, strong magnets are used. This reduces the need for perfect alignment and improves reliability even if there’s some mechanical play over time.
Another bonus? Reed switches are naturally sealed against dust, moisture, and other environmental factors. Unlike traditional mechanical limit switches that need extra protective casings, reeds are ready to handle tough conditions right out of the box.
Explosion-Proof and Hazardous Environments
Because of their sealed design, reed switches are a go-to choice in environments where sparks could be dangerous—like chemical plants or fuel storage facilities. Their contactless activation minimizes the risk of ignition.
Plus, using contactless control circuits improves both safety and lifespan:
- Less wear and tear for longer service life
- No electromagnetic interference since there are no sparking contacts
Contactless Reed Switches
While the term might be a bit misleading (since the internal contacts still move), the contactless activation through magnetic fields makes these switches super versatile. You’ll find them everywhere:
- Security systems: Great for detecting open windows, doors, and hatches
- Access control: Sensing door positions or people passing through
- Fluid level sensors: Thanks to their waterproof, sealed design
They’re affordable, easy to integrate, and reliable. Reed relays, whether standalone or built into other devices, are a practical solution in countless applications.
In Conclusion
Reed switches cover a wide range of devices, all playing key roles in control and automation systems. Whether you’re automating a gate, securing a building, or managing an industrial process, these little switches punch way above their weight.
For more automation solutions and top-quality security products, check out safsale.com—your go-to for smart, reliable tech.