📶 Enhancing WiFi & GSM Signals: Organizational and Hardware Solutions for Robust Wireless Connectivity
In today’s connected world, reliable WiFi and GSM signals are as essential as electricity in your home. However, in both urban and rural settings across the United States, interference and obstacles can weaken your wireless signal. Whether you're streaming video on your laptop or managing a remote security system, enhancing your WiFi and GSM signals can dramatically improve performance. In this guide, we cover both organizational methods and hardware solutions to boost your signal quality, ensuring a strong, stable connection for all your devices.
🔍 Understanding the Factors Affecting Signal Quality
The strength of your WiFi or GSM signal is influenced by several factors:
- Distance: The farther you are from the router (for WiFi) or the cell tower (for GSM), the weaker the signal. For example, while a WiFi router might effectively cover up to 150 feet in open areas, signal loss is inevitable as distance increases.
- Obstructions: Walls, trees, and other obstacles can significantly diminish signal strength. In buildings, even a standard brick wall can reduce WiFi range by about 25%.
- Interference: Devices such as microwaves, cordless phones, and even neighboring routers can generate electromagnetic noise that disrupts WiFi or GSM signals.
- Network Load: The more devices connected to a single router or cell tower, the more the available bandwidth is divided among them.
🏠 Organizational Methods to Boost WiFi and GSM Signals
Before investing in additional hardware, simple adjustments in the setup can greatly improve your signal quality:
1. Optimal Placement
- Router Location:
Place your WiFi router in a central, elevated position-near a window or on a higher floor-to maximize coverage. For rural homes or cabins, mounting the router near an exterior wall can help. - Minimize Obstructions:
Avoid placing routers near large metal objects or devices that generate interference, such as microwaves or wireless speakers.
2. Channel Optimization
- Select a Clear Channel:
WiFi routers operate on various channels within the 2.4 GHz band (and 5 GHz for newer devices). Use free tools like inSSIDer to identify less congested channels, and manually set your router to operate on these channels. - Reduce Interference:
Changing the channel can help avoid overlap with other wireless networks and nearby electronic devices.
3. Firmware and Driver Updates
- Keep Software Current:
Regularly update your router’s firmware and the drivers for wireless devices. Manufacturers often release updates that improve performance, security, and compatibility with new standards.
🔧 Hardware Solutions for Signal Enhancement
When organizational methods aren’t enough, consider these hardware solutions to boost your wireless signals:
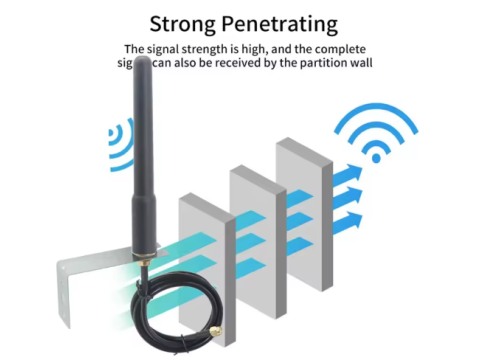
1. Directional Antennas
- How They Work:
Directional antennas focus the radio signal in one direction rather than broadcasting it uniformly. This results in higher gain and longer range in the target direction. - Application:
For GSM enhancement, a Yagi (wave channel) or panel antenna can be used to improve reception from distant cell towers. Similarly, for WiFi, a directional antenna helps cover larger outdoor areas or specific zones in a building. - Key Metric - Gain:
Gain is measured in dBi (decibels over isotropic). For example, a 6 dBi antenna roughly doubles the signal strength, while a 10 dBi model can increase it tenfold in the desired direction.
2. Repeaters and Signal Boosters
- WiFi Repeaters:
A WiFi repeater (or extender) receives your router’s signal and rebroadcasts it, effectively increasing your coverage area. These devices are especially useful in large homes or offices. - GSM Signal Boosters:
Also known as amplifiers or repeaters, GSM boosters capture weak cellular signals, amplify them, and retransmit them to your devices.- Consideration:
Ensure your booster supports the relevant frequency bands (e.g., 800, 1800, or 2600 MHz for 4G) and is designed for your specific environment.
- Consideration:
3. DIY Signal Amplifiers
- Simple Projects:
Some enthusiasts attempt to build their own WiFi signal amplifiers using everyday materials-like modifying a metal can into a rudimentary directional antenna. - Caution:
While these projects can offer a slight improvement, they rarely match the performance of professionally engineered solutions. For critical applications, it’s best to invest in certified equipment.
📶 Enhancing WiFi vs. GSM: Key Differences
While both WiFi and GSM signal enhancements follow similar principles, they differ mainly in their scale and application:
- GSM Signals:
GSM networks benefit from extensive cell towers that cover large distances (often up to 75 miles in open areas). However, in urban areas with high interference or in remote rural settings, boosting GSM signals may require directional antennas or signal boosters. - WiFi Signals:
WiFi is designed for short-range, high-speed data transfer. In buildings, the signal might only extend 150 feet at best under ideal conditions. Enhancements often focus on optimizing router placement and using extenders to cover dead zones.
🎯 Conclusion
Improving WiFi and GSM signal quality involves both strategic organizational choices and targeted hardware solutions. By placing routers and antennas optimally, selecting the right channels, updating firmware, and employing devices like directional antennas, repeaters, or professional-grade boosters, you can significantly enhance your network's performance.
At safsale.com, we offer a range of high-quality, American-standard wireless devices designed to boost your WiFi and GSM signals, whether you’re in a busy urban apartment or a remote country cabin. Enhance your connectivity today and enjoy faster, more reliable wireless internet-no matter where you are 🚀📶🔧
Explore our solutions now and experience the difference in wireless performance!