Stepper Motors: Functionality, Types & Practical Uses
Stepper motors are electromechanical devices that convert electrical pulses into precise mechanical movement. Unlike traditional electric motors that rotate continuously, stepper motors move in fixed steps, providing high precision positioning without the need for feedback sensors.
🔹 Key Features of Stepper Motors
✔ Discrete movement – Controlled step-by-step rotation
✔ Accurate positioning – Ideal for CNC machines and robotics
✔ Holding torque – Can maintain position under load
✔ Open-loop control – No need for position feedback
📌 These characteristics make stepper motors essential for automation, robotics, and precision motion control.
1️⃣ How Stepper Motors Work
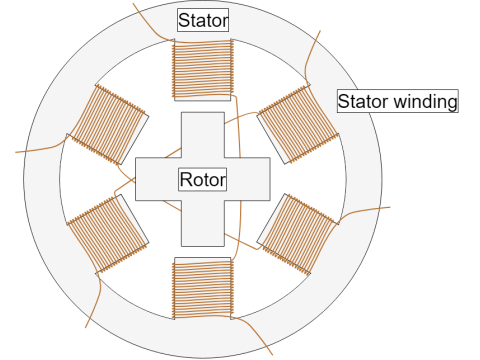
Stepper motors function based on electromagnetic interaction between the stator and rotor.
🔹 Stepper Motor Structure
1️⃣ Stator – Stationary part with multiple electromagnetic coils
2️⃣ Rotor – Rotating part made of permanent magnets or toothed ferromagnetic material
3️⃣ Control System – Sends electrical pulses to the stator to energize coils in sequence
✔️ Step-by-Step Rotation
Each electrical pulse sent to the motor activates a different coil, pulling the rotor into alignment with the electromagnetic field. This incremental motion results in highly controlled positioning.
| Step Type | Step Angle (Degrees) |
|---|---|
| Standard Step | 1.8° (200 steps/rev) |
| Half Step | 0.9° (400 steps/rev) |
| Microstep | < 0.9° (up to 256 microsteps per step) |
📌 Microstepping allows for smoother motion and finer resolution.
2️⃣ Types of Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are classified based on rotor design and control method.
✔️ 1. Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor
✔ Uses a rotor made of permanent magnets
✔ Provides moderate torque & accuracy
✔ Step angles: 7.5° to 15° per step
📌 Ideal for small precision applications like printers and cameras.
✔️ 2. Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor
✔ Rotor has no permanent magnets
✔ Movement depends on minimizing magnetic resistance
✔ Larger step angles: 15° to 30° per step
📌 Lower torque but cost-effective for simple automation systems.
✔️ 3. Hybrid Stepper Motor (Most Common)
✔ Combines permanent magnet & variable reluctance designs
✔ Offers high precision (0.9° to 1.8° per step)
✔ Provides better torque & speed performance
📌 Widely used in CNC machines, 3D printers, and industrial automation.
📌 Hybrid stepper motors are the most advanced and commonly used due to their high torque and precision.
3️⃣ Stepper Motor Operating Modes
Stepper motors can operate in different modes depending on how the stator windings are energized.
✔️ 1. Full-Step Mode
✔ Moves one full step per pulse
✔ Maximizes holding torque
✔ Can cause vibration at low speeds
📌 Best for applications that require strong torque rather than smooth motion.
✔️ 2. Half-Step Mode
✔ Moves in half-step increments
✔ Provides twice the resolution of full-step mode
✔ Reduces vibration compared to full-step mode
📌 Balances torque and smooth motion.
✔️ 3. Microstepping Mode (Most Advanced)
✔ Divides each step into smaller microsteps (up to 256 microsteps per step)
✔ Smoothest motion with minimal vibration
✔ Requires advanced stepper drivers
📌 Ideal for high-precision applications like CNC and robotics.
4️⃣ Applications of Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are used in a wide range of industries, from 3D printing to aerospace applications.
✔️ 1. CNC Machines & 3D Printers
✔ Stepper motors control the movement of cutting tools and printing heads
✔ Provide high precision and repeatability
📌 Used in CNC milling, laser cutting, and additive manufacturing.
✔️ 2. Robotics & Automation
✔ Enables precise movement of robotic arms and conveyor belts
✔ Provides accurate positioning for pick-and-place machines
📌 Essential for industrial robots and robotic automation.
✔️ 3. Office Equipment
✔ Used in printers, scanners, and photocopiers
✔ Controls paper feeding and print head positioning
📌 Ensures consistent operation in office environments.
✔️ 4. Medical Equipment
✔ Found in MRI scanners, lab automation, and infusion pumps
✔ Ensures precise control of medical instruments
📌 Critical for high-precision applications in healthcare.
✔️ 5. Aerospace & Defense
✔ Stepper motors are used in satellite positioning and defense systems
✔ Reliability and precision make them ideal for extreme environments
📌 Common in missile guidance systems and space exploration technology.
5️⃣ Maintenance & Troubleshooting Stepper Motors
Proper maintenance is crucial for extending stepper motor lifespan.
✔️ Best Practices for Maintenance
✔ Ensure proper cooling to prevent overheating
✔ Avoid mechanical overloads that can damage bearings
✔ Use appropriate drivers to prevent overcurrent damage
✔️ Common Stepper Motor Issues & Solutions
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Motor not moving | Faulty wiring or driver issue | Check connections & driver settings |
| Skipping steps | Overload or low voltage | Reduce load or increase voltage |
| Overheating | Excessive current or poor ventilation | Use proper cooling system |
| Vibration & noise | Low stepping resolution | Use microstepping mode |
📌 Regular checks and proper setup will ensure long-term reliability and performance.
6️⃣ Choosing the Right Stepper Motor
✔️ Key Factors to Consider
✔ Step Angle – Determines motion precision
✔ Torque Requirements – Higher torque for heavier loads
✔ Voltage & Current Ratings – Ensure compatibility with drivers
✔ Size & Mounting Type – Fit your application requirements
📌 For high-precision applications, choose hybrid stepper motors with microstepping drivers.
🔟 Conclusion: The Future of Stepper Motors
✅ Stepper motors provide accurate and reliable motion control for automation and robotics.
✅ Microstepping technology enhances performance by reducing vibration.
✅ Hybrid stepper motors dominate due to their balance of torque and precision.
🚀 As industries move toward smart automation, stepper motors will continue to play a crucial role in precision motion control!