What Is an Electric Circuit? Basics, Components & Types
An electric circuit is a closed-loop system that allows the flow of electric current through interconnected components. Electric circuits play a fundamental role in power generation, transmission, and distribution, as well as in control and signal processing systems.
This article covers the basic concepts of electric circuits, their main components, and different types of circuits used in electrical and electronic systems.
Understanding the Basics of an Electric Circuit
An electric circuit consists of conductors, power sources, and electrical components that enable current flow and energy conversion.
Electric circuits perform several functions, including:
✅ Powering electrical devices (lights, motors, heating elements)
✅ Controlling the flow of electricity (switches, relays)
✅ Measuring electrical parameters (voltmeters, ammeters)
✅ Transmitting signals (communication systems)
A basic electric circuit consists of:
✔ Power Source - Provides the electrical energy (e.g., battery, generator)
✔ Conductors - Wires that allow current flow
✔ Load (Resistor, Motor, Light, etc.) - Consumes electrical energy
✔ Control Devices - Switches, relays, circuit breakers
For an electric circuit to function, it must be a closed loop. If the circuit is open, current will not flow.
1️⃣ Components of an Electric Circuit
✔️ Power Source (Voltage Supply)
Electric circuits require a power source to generate the voltage that drives current through the circuit.
Examples:
✅ Batteries
✅ Generators
✅ Power adapters
✅ Solar panels
Power sources convert energy (chemical, mechanical, or solar) into electrical energy.
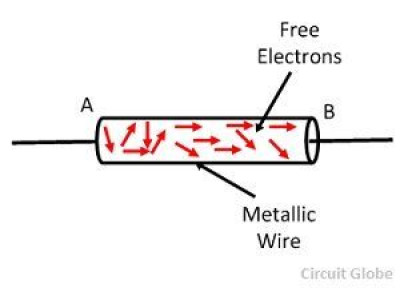
✔️ Conductors (Wires & Cables)
Conductors connect components in the circuit, allowing electric current to flow.
Common conductor materials:
✅ Copper - Most widely used due to high conductivity
✅ Aluminum - Used in power transmission
✅ Gold & Silver - Used in high-precision electronics
Conductors must have low resistance to ensure efficient current flow.
✔️ Load (Electrical Devices)
A load is any device that consumes electrical energy and converts it into another form (light, heat, motion, etc.).
Common loads:
✅ Resistors - Convert electricity into heat
✅ Motors - Convert electricity into mechanical motion
✅ Lamps/LEDs - Convert electricity into light
✅ Speakers - Convert electricity into sound
Loads create resistance in the circuit, regulating the amount of current flow.
✔️ Control & Protection Devices
Control and protection devices regulate the circuit’s operation and prevent damage from overloads or short circuits.
Examples:
✅ Switches - Open or close a circuit manually
✅ Relays - Electrically operated switches
✅ Fuses & Circuit Breakers - Prevent overload damage
✅ Diodes - Allow current to flow in one direction only
Protection devices are critical for circuit safety and longevity.
2️⃣ Key Terms in Electric Circuits
Understanding the following terms is essential for analyzing circuits:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | Electrical potential difference (measured in volts) |
| Current (I) | Flow of electric charge (measured in amperes) |
| Resistance (R) | Opposition to current flow (measured in ohms) |
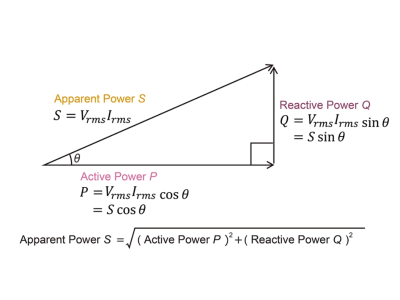
| Power (P) | Rate of energy consumption (measured in watts) |
| Ohm’s Law | V = I × R (Voltage = Current × Resistance) |
3️⃣ Types of Electric Circuits
Electric circuits are categorized based on function and configuration.
✔️ 1. Based on Function
Power Circuits - Used for generating, transmitting, and distributing power (e.g., electrical grids, industrial motors).
Control Circuits - Used to operate electrical devices (e.g., switch circuits, automation systems).
Signal Circuits - Used in communication and data transmission (e.g., telephone networks, computer processors).
Measurement Circuits - Used in monitoring electrical parameters (e.g., voltage meters, current sensors).
Different types of circuits serve various purposes, from powering machines to processing signals.
✔️ 2. Based on Configuration
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
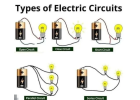
| Series Circuit | Components are connected end-to-end, sharing the same current | Christmas lights |
| Parallel Circuit | Components are connected across the same voltage source, each receiving equal voltage | Household wiring |
| Series-Parallel Circuit | A mix of both series and parallel elements | Automotive circuits |
| Open Circuit | A circuit with a break, preventing current flow | A switch in OFF position |
| Closed Circuit | A complete circuit where current flows uninterrupted | A working light bulb |
| Short Circuit | A low-resistance connection causing excessive current flow | Electrical fault |
Parallel circuits are commonly used in home wiring, while series circuits are used in applications like LED strips.
4️⃣ Real-World Applications of Electric Circuits
Electric circuits are everywhere, powering our daily lives.
✔️ Household Applications
✅ Lighting Systems - Powering bulbs and LEDs
✅ Home Appliances - Refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners
✅ HVAC & Heating Systems - Thermostats, electric heaters
✔️ Industrial & Commercial Applications
✅ Manufacturing - Industrial machines, conveyor belts
✅ Power Transmission - Electrical grids, transformers
✅ Automation & Robotics - Programmable control circuits
✔️ Automotive & Transport Applications
✅ Vehicle Electrical Systems - Car batteries, ignition systems
✅ Electric Vehicles (EVs) - Motor controllers, battery management systems
✅ Aerospace & Railways - Navigation and control circuits
Electric circuits are essential in all technological advancements, from home automation to space exploration.
5️⃣ Conclusion: Why Understanding Circuits Matters
Electric circuits form the foundation of electrical and electronic systems.
✔ Knowing how circuits work helps in designing, troubleshooting, and optimizing electrical devices.
✔ Different circuit types serve specific functions, from power distribution to control and automation.
✔ Electrical safety measures, such as fuses and circuit breakers, prevent accidents and damage.
With advancements in smart technology and renewable energy, understanding circuits is more important than ever!