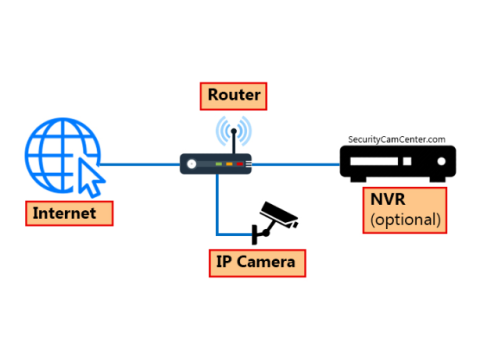
What Is an IP Camera and How Does It Work?
IP cameras are cutting-edge surveillance tools that offer advanced capabilities compared to traditional analog cameras. From remote monitoring to high-quality video recording, these cameras use Internet Protocol (IP) for efficient data transmission and integration into modern security systems.
How IP Cameras Work
An IP camera converts optical images into digital signals, transmitting them over a network. Unlike analog cameras, IP cameras can function autonomously and support advanced configurations.
Here’s a simplified overview of its core components:
- Lens: Captures the scene and directs light to the image sensor.
- Image Sensor: Converts light into electrical signals (common types include CMOS or CCD).
- Processor: Handles tasks like compression, motion detection, and video encoding (H.264 or MJPEG).
Connectivity Options
IP cameras support multiple data transmission methods:
- Ethernet (Wired): The most reliable option, using standard Cat5/Cat6 cables.
- WiFi (Wireless): Convenient but may face range and signal stability issues, especially beyond 30-50 feet.
- Fiber Optic: Ideal for large-scale systems requiring high-speed data over long distances.
For most home and business setups, Ethernet is the go-to solution due to its reliability and scalability.
Advantages of IP Cameras
Multi-Device Integration:
Connect multiple cameras to a single line using network switches. A single system can support up to 10 devices, depending on the network’s bandwidth.Remote Monitoring:
Access live feeds and recordings from multiple devices (PCs, smartphones) with proper user permissions and software.Cloud Integration:
IP cameras often integrate with cloud-based platforms, making remote access and storage seamless without requiring a dedicated IP address.
Top Features of IP Cameras
Onboard Storage:
Many models support microSD cards for local video storage, ensuring data isn’t lost during network interruptions.Motion Detection:
Advanced models have built-in motion sensors, enabling recordings to start only when movement is detected, reducing storage use.Audio Recording:
Options include:- Built-in microphones for ambient audio.
- Ports for external microphones for higher-quality sound capture.
High Scalability:
Perfect for both small and large installations, from a single camera to expansive networks spanning multiple locations.
When to Choose IP Cameras
IP cameras excel in settings requiring high-quality video, remote access, and flexible system scalability. While analog cameras may suffice for smaller projects with limited budgets, IP systems are the future of surveillance, offering unparalleled convenience and functionality.
Explore a range of IP cameras and security solutions tailored to your needs on safsale.com