Surveillance Cameras: Outdoor, Indoor, and Key Features
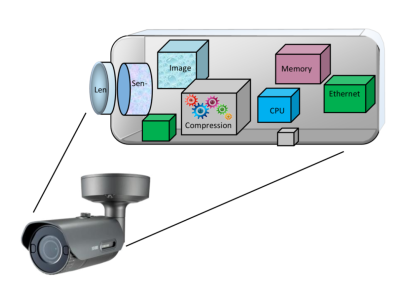
Surveillance cameras are essential for transforming optical images into electrical signals, enabling real-time monitoring and recording for enhanced security. These systems come in two primary types: analog and IP (network) cameras.
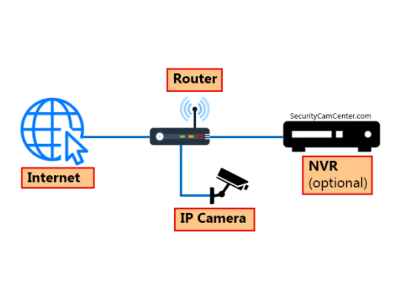
While analog cameras transmit video via coaxial cables, IP cameras function as network devices, capable of transmitting data over the internet or local networks.
Types of Surveillance Cameras
Outdoor Surveillance Cameras
Outdoor cameras are designed to withstand harsh environments and require:
- Dust and water protection: Minimum IP66 rating.
- Temperature resistance: Some models include heating or cooling systems.
- Anti-vandal features: Durable housings to protect against intentional damage.
Outdoor installations may face unique challenges like extreme weather conditions, falling debris, or vandalism, making robust and secure mounting solutions critical.
Indoor Surveillance Cameras
Indoor cameras are widely used for homes, offices, and public spaces. Common designs include:
Dome Cameras:
- Sleek design minimizes disruption to interior aesthetics.
- Easily installed on ceilings or walls with concealed wiring.
Cylinder Cameras: Offer adjustable focus and are ideal for targeted areas.
Miniature Cameras: Perfect for discreet monitoring or hidden installations.
Key Features of Surveillance Cameras
1. Resolution and Clarity
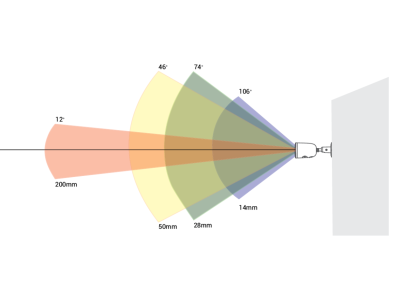
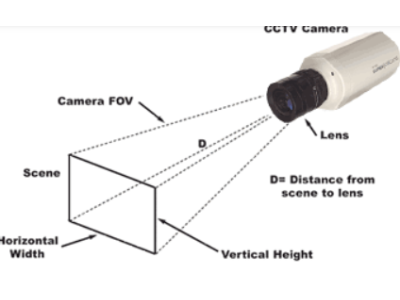
- Standard options range from 2MP (1080p) to 8MP (4K), with higher resolutions offering greater detail.
2. Light Sensitivity (Lux Rating)
- Indicates the minimum illumination required for operation. Lower lux ratings mean better performance in low-light conditions.
3. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (S/N)
- A higher ratio (>45 dB) ensures clear images with minimal noise.
4. Automatic Features:
- Auto-Iris (AR): Adjusts to changing light conditions.
- Electronic Shutter (ES): Controls light exposure for clearer images.
- Backlight Compensation (BLC): Prevents shadows when viewing against bright light.
5. Infrared (IR) Capabilities
- Essential for night vision, enabling monitoring in complete darkness.
6. Weather and Damage Protection
- Outdoor cameras should have robust housings for protection against weather and vandalism.
Choosing the Right Camera for Your Needs
- Environment: Indoor or outdoor? Ensure appropriate IP ratings for weather resistance.
- Purpose: Identify the goal (e.g., general monitoring, facial recognition, license plate reading).
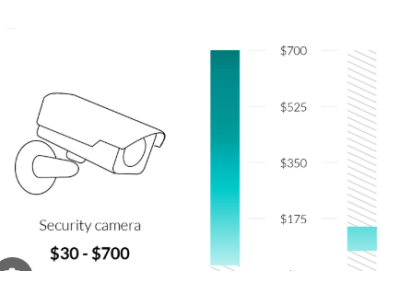
- Budget: Analog cameras are typically more affordable, while IP cameras offer scalability and advanced features.
- Connectivity: Decide between wired, wireless, or hybrid systems based on infrastructure and ease of installation.
Conclusion
Surveillance cameras are a cornerstone of modern security systems, offering diverse options for various needs. Understanding the types, features, and installation requirements ensures you choose the right system for your environment.
Investing in quality cameras and proper installation not only enhances security but also provides peace of mind, whether at home, in the office, or outdoors.