Surveillance Camera Viewing Angle: A Key Parameter
The viewing angle determines the area a camera can monitor. It is directly influenced by the focal length of the lens and the sensor size of the camera.
How Viewing Angle Depends on Sensor Size and Focal Length
Sensor Size:
- Cameras with larger sensors have wider viewing angles for the same focal length.
- For example, a camera with a 1/2-inch sensor will capture a wider scene than one with a 1/4-inch sensor.
Focal Length:
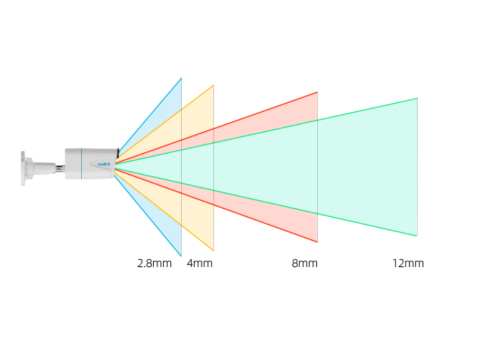
- Short focal length = Wide-angle view.
- Long focal length = Narrow-angle view.
- A wide-angle lens captures a broader area but sacrifices detail, while a long-focus lens provides greater detail over a smaller area.
Choosing the Right Viewing Angle
General Monitoring
- Use a wide-angle lens for areas like parking lots or store entrances where the goal is to monitor overall activity.
- Examples: 2.8mm or 4mm lenses provide wide fields of view.
Detailed Observation
- Use a narrow-angle lens to focus on specific areas, such as cash registers or entry points, where identifying individuals or objects is crucial.
- Examples: 12mm or higher lenses.
Field of View Calculations
The relationship between viewing angle and field of view can be calculated:
Formula for Focal Length:
Where:
- : Focal length of the lens (mm).
- : Distance to the object (m).
- : Sensor size (horizontal or vertical, mm).
- : Object size (horizontal or vertical, m).
Adjusting for Partial Screen Coverage:
To calculate for part of the screen:
Where:
- : Percentage of screen occupied by the object.
The final formula becomes:
Practical Advice
Wide-Angle Lenses:
- Great for covering large spaces.
- Lower detail for distant objects.
Narrow-Angle Lenses:
- Better for zooming in on specific zones.
- Limited coverage area.
Other Considerations
- Depth of Field: The range in which objects remain in focus. Affects the clarity of objects at varying distances.
- Online Tools: Use an online viewing angle calculator for precise calculations tailored to your system.
Conclusion
Selecting the right viewing angle ensures effective monitoring tailored to your needs. Whether prioritizing wide-area coverage or high-detail observation, understanding the relationship between focal length, sensor size, and field of view is crucial.
Surveillance Camera Resolution
11/01/2025
Wide-Angle Security Cameras
11/01/2025