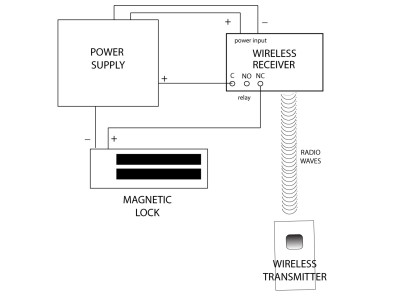
Electric Door Locks are pivotal components in modern Access Control and Management Systems (ACMS), providing enhanced security by regulating entry and exit points through electronic means. These locks are often integrated with other security devices such as surveillance cameras, controllers, and code-based entry systems to form comprehensive security solutions for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. This guide explores the various types of electric door locks, their operational principles, advantages and disadvantages, installation considerations, and best practices to ensure optimal security and functionality in compliance with American standards.
Types and Features of Electric Door Locks
Electric door locks can be categorized based on their operational principles, external appearance, and installation methods. The primary types include Electromagnetic Locks and Electromechanical Locks. Additionally, there are specialized locks designed for Interior Doors. Each type offers unique functionalities suited to different security needs and environments.
Electromagnetic Locks
Overview
Electromagnetic Locks (Maglocks) operate on the principle of electromagnetic force to secure doors. They consist of two main components:
- Electromagnet: Mounted on the door frame, this component generates a magnetic field when energized.
- Armature Plate: Attached to the door, it is attracted to the electromagnet, creating a strong hold that keeps the door closed.
Maglocks maintain an unbroken connection as long as power is supplied, ensuring secure closure. They are typically powered by low-voltage sources (12V or 24V) to minimize the risk of electric shock.
Advantages
Simplicity and Ease of Installation:
- Straightforward design with minimal moving parts.
- Quick and easy to install, often requiring only mounting on the door and frame.
High Holding Force:
- Capable of securing doors with significant strength, suitable for high-traffic areas.
Durability and Low Maintenance:
- Long operational life due to the absence of mechanical components that can wear out.
- Resistant to tampering and physical attacks.
Compatibility with Smart Systems:
- Easily integrates with various access control systems, including keypads, card readers, and biometric scanners.
Disadvantages
Dependence on Power Supply:
- Requires continuous power to remain locked. In case of power failure, the door remains unlocked, posing security risks.
- Mitigation requires backup power solutions such as Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) or batteries.
Limited Mechanical Security:
- Lack of mechanical locking means they can be less secure in environments where power stability cannot be guaranteed.
No Physical Barrier:
- Does not provide a physical barrier against forced entry beyond the magnetic hold.
Electromechanical Locks
Overview
Electromechanical Locks combine electronic control with mechanical locking mechanisms, typically using solenoids or motors to engage or disengage the lock. They offer both fail-safe and fail-secure operations, providing versatility in security management.
Types of Electromechanical Locks
Electro-Blocking Locks:
- Utilize a complex arrangement of levers, springs, and solenoids to control the locking mechanism.
- Remain locked by default and require power to unlock.
Solenoid Locks:
- Feature a solenoid-driven latch that retracts when energized, allowing the door to open.
- Typically fail-secure, meaning they remain locked when power is lost.
Motorized Locks:
- Incorporate small electric motors to move the locking mechanism.
- Offer high durability and reliability, suitable for high-security applications.
Advantages
Fail-Secure and Fail-Safe Options:
- Can be configured to lock or unlock during power outages, enhancing security based on specific needs.
Enhanced Security Features:
- More resistant to forced entry due to the presence of mechanical components.
- Often includes additional security layers such as anti-tampering features.
Versatile Installation:
- Suitable for a wide range of door types and security requirements, from residential to industrial applications.
Integration Capabilities:
- Easily integrates with advanced access control systems, including multi-factor authentication and centralized management.
Disadvantages
Higher Cost:
- More expensive than electromagnetic locks due to the complexity of mechanical components.
Complex Installation:
- Requires precise alignment and integration with both mechanical door components and electronic systems.
- Often necessitates professional installation to ensure optimal performance.
Maintenance Requirements:
- Mechanical parts may require regular maintenance to ensure longevity and proper functioning.
Power Consumption:
- Generally consume more power than electromagnetic locks, necessitating robust power supply solutions.
Magnetic Locks for Interior Doors
Overview
Magnetic Locks for Interior Doors are specialized versions of electromagnetic locks designed for internal applications. They provide secure access control within buildings, offering both active and passive locking mechanisms.
Active Magnetic Locks:
- Operate similarly to external electromagnetic locks, requiring continuous power to maintain the locked state.
- Suitable for environments where security needs are high, and power reliability is ensured.
Passive Magnetic Locks:
- Utilize a movable magnet that engages when the door is closed.
- Do not require continuous power to remain locked, offering a balance between security and energy efficiency.
Advantages
Reliable Security for Internal Access:
- Provide robust security for internal doors, preventing unauthorized access within buildings.
Low Energy Consumption:
- Passive locks consume less power as they do not require continuous energy to maintain the locked state.
Seamless Integration:
- Can be integrated with various access control methods, including keypads, proximity cards, and biometric systems.
Aesthetic Appeal:
- Minimalistic design that does not interfere with the door’s appearance, making them ideal for modern interior applications.
Disadvantages
Dependence on Power for Active Locks:
- Similar to external electromagnetic locks, active interior magnetic locks require a reliable power supply to maintain security.
Limited Physical Barrier:
- Do not provide a substantial physical barrier beyond the magnetic hold, making them less suitable for high-security environments without additional measures.
Installation Complexity:
- Requires careful installation to ensure alignment and proper functioning within the door and frame.
Installation Considerations
Proper installation of electric door locks is crucial to ensure their effectiveness and longevity. Consider the following factors when installing electromagnetic and electromechanical locks:
1. Power Supply
- Reliable Power Source: Ensure that the lock is connected to a stable power source. For electromagnetic locks, consider implementing backup power solutions such as UPS or battery backups to maintain security during power outages.
- Separate Power Circuits: It is advisable to use separate power circuits for controllers and locking mechanisms to prevent interference and ensure system stability.
2. Wiring and Cabling
- Appropriate Gauge Cables: Use cables with sufficient gauge to handle the current requirements of the lock, especially for electromechanical locks that may draw higher currents during activation.
- Concealed Cabling: Run cables through concealed pathways such as walls or conduits to prevent tampering and maintain aesthetic appeal.
3. Mounting and Alignment
- Precise Alignment: Ensure that the electromagnet and armature plate (for electromagnetic locks) or the mechanical components (for electromechanical locks) are precisely aligned to achieve maximum holding force and reliable operation.
- Secure Mounting: Use appropriate mounting hardware to secure the lock components firmly to the door and frame, preventing movement or misalignment over time.
4. Integration with Access Control Systems
- Compatibility: Verify that the electric door lock is compatible with the existing access control system, including controllers, readers, and software.
- System Configuration: Properly configure the access control system to recognize and manage the electric door locks, ensuring seamless operation and security management.
5. Compliance with Standards
- Building Codes: Adhere to local building codes and regulations regarding the installation of electric door locks, ensuring safety and compliance.
- Electrical Standards: Follow the National Electrical Code (NEC) and other relevant electrical standards to ensure safe and reliable electrical connections.
Best Practices for Electric Door Locks
Implementing electric door locks effectively requires adherence to best practices to maximize security and system performance:
1. Redundancy and Backup Systems
- Dual Locking Mechanisms: Consider installing multiple locking mechanisms (e.g., both electromagnetic and electromechanical locks) to provide redundancy and enhance security.
- Backup Power: Ensure that backup power systems are in place to maintain lock functionality during power outages, especially for high-security environments.
2. Regular Maintenance
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of electric door locks to identify and address any signs of wear, misalignment, or electrical issues.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Keep mechanical components clean and properly lubricated to ensure smooth operation and prevent malfunctions.
3. Security Enhancements
- Anti-Tampering Features: Choose locks with built-in anti-tampering features to prevent unauthorized manipulation or forced entry.
- Secure Wiring: Protect wiring and connections against physical damage and tampering by using protective conduits and secure routing methods.
4. User Training and Access Management
- Comprehensive Training: Provide training for users and administrators on the proper use and management of electric door locks, ensuring that access control policies are followed.
- Access Permissions: Regularly review and update access permissions to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to secured areas.
5. Integration with Other Security Systems
- Surveillance Cameras: Integrate electric door locks with surveillance cameras to monitor and record access attempts, enhancing overall security.
- Alarm Systems: Connect locks to alarm systems to trigger alerts in case of unauthorized access or security breaches.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Relevant Standards:
- NFPA 72 - National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code: Governs the design, installation, and maintenance of fire alarm and signaling systems, including aspects related to ACMS integration.
- National Electrical Code (NEC): Regulates the electrical aspects of alarm system installations to ensure safety and compliance.
- UL Standards: Provide safety and performance requirements for security alarm devices and components.
- OSHA Standards (29 CFR 1910): Include fire safety regulations for workplaces, covering the installation and maintenance of fire alarm systems to protect employees.
- Local Building Codes: Additional requirements specific to your locality must also be adhered to for compliance and safety.
Key Compliance Points:
- Power Supply Design: Ensure all power supplies meet the electrical requirements outlined in NEC and UL standards, including proper grounding and protection mechanisms.
- Cable Management: Adhere to guidelines for cable routing, minimizing exposure and protecting against physical damage or tampering.
- System Integration: Ensure that all ACS components are correctly integrated with other security and safety systems for coordinated operation.
- Documentation and Certification: Maintain detailed records of power supply installations, configurations, and compliance certifications to demonstrate adherence to relevant standards.
- Emergency Power Solutions: Implement backup power systems (e.g., UPS, batteries) in compliance with NFPA 72 to ensure system functionality during emergencies.
Final Thoughts
Electric Door Locks are essential for modern Access Control and Management Systems (ACMS), offering a blend of electronic control and mechanical security to safeguard premises effectively. Understanding the distinctions between Electromagnetic and Electromechanical locks, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages, enables organizations to make informed decisions tailored to their security needs. Adhering to best practices in installation, maintenance, and system integration ensures that electric door locks perform reliably and contribute to a robust security infrastructure.
Key Takeaways:
- Choose the Right Lock Type: Assess the specific security requirements of your facility to determine whether electromagnetic or electromechanical locks are more suitable.
- Ensure Reliable Power Supply: Implement stable and backup power solutions to maintain lock functionality during power outages, especially for fail-safe applications.
- Prioritize Proper Installation: Ensure precise alignment and secure mounting of lock components to maximize holding force and prevent operational issues.
- Integrate with Comprehensive Security Systems: Combine electric door locks with other security measures like surveillance cameras and alarm systems for enhanced protection.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Schedule routine maintenance to ensure the longevity and reliability of electric door locks, addressing any wear or electrical issues promptly.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhere to relevant electrical and building codes to ensure safe and legally compliant installations.
- User Training and Access Management: Educate users and administrators on proper lock usage and access control policies to maintain system integrity.
- Invest in Security Enhancements: Utilize anti-tampering features and secure wiring practices to protect against unauthorized access and system manipulation.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain thorough documentation of installations, configurations, and compliance certifications for accountability and regulatory adherence.
- Professional Installation and Support: Engage certified security professionals for the installation and configuration of electric door locks to ensure optimal performance and compliance.
For expert assistance in selecting and installing electric door locks, ensuring compliance with relevant standards, or accessing comprehensive project documentation, visit safsale.com. Our specialists are ready to help you design and deploy reliable, compliant, and efficient access control solutions tailored to your specific security needs.
Important Notice on Standards
All referenced documents and standards in this guide are provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as official publications. For authoritative guidelines and legal requirements, always consult the official standards organizations or regulatory bodies.