Electromagnetic Locks (EMLs) are fundamental components in modern Access Control and Management Systems (ACMS), offering robust security solutions for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Properly connecting and configuring these locks is crucial to ensure their reliability, security, and seamless integration with existing security infrastructure. This guide provides a detailed overview of the connection schematics for electromagnetic locks, including essential components, wiring diagrams, controller integration, and best practices to ensure a secure and efficient installation in compliance with American standards.
Understanding Electromagnetic Lock Connections
Electromagnetic locks operate by using an electromagnet and an armature plate to secure doors. The connection schematic for an EML typically involves integrating the lock with a power supply, an exit button, and a controller or access panel. Understanding how these components interact is essential for a successful installation.
Key Components
Electromagnetic Lock (EML):
- Electromagnet: Mounted on the door frame, it generates a magnetic field when energized.
- Armature Plate (Yarmo): Attached to the door, it is attracted to the electromagnet, creating a strong hold that keeps the door closed.
Power Supply:
- Provides the necessary voltage (typically 12V or 24V DC) to energize the electromagnet.
- Must match the EML’s voltage requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Exit Button:
- Allows authorized individuals to exit the secured area by de-energizing the electromagnet.
- Typically connected to the controller to send a signal for unlocking.
Controller:
- Manages the operation of the EML based on inputs from access devices (e.g., keypads, card readers).
- Examples include models like Z-5R for standalone systems and S2000-2 for networked systems.
Intercom Panel (Optional):
- Used in conjunction with EMLs to control access via audio or video communication.
- Some panels may require additional relays or controllers for compatibility with EMLs.
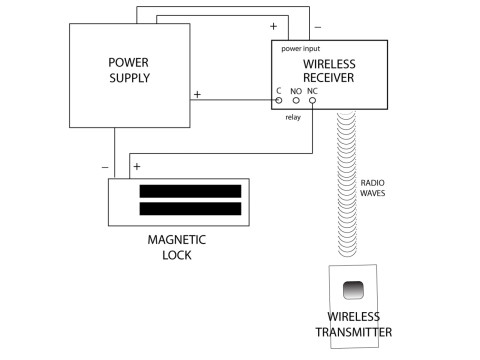
Connection Diagram Overview
The classic connection schematic for an electromagnetic lock involves connecting the EML to a power supply, exit button, and controller. Below is a textual representation of the typical wiring diagram (Figure 1):
Figure 1: Electromagnetic Lock Connection Diagram
Components Explanation:
- Power Supply (+12V DC): Connects to the positive terminal of the EML.
- EML: The electromagnet that holds the door closed when energized.
- Controller: Receives signals from access devices and controls the EML accordingly.
- Exit Button: When pressed, it sends a signal to the controller to deactivate the EML, allowing the door to open.
- Ground (GND): Common ground connection for all components.
Step-by-Step Connection Process
1. Mounting the Electromagnetic Lock
Positioning:
- Mount the electromagnet on the door frame at a height that aligns with the armature plate on the door.
- Ensure precise alignment to maximize holding force and prevent door sagging.
Securing:
- Use mounting brackets and screws provided in the lock kit to secure the electromagnet firmly to the frame.
- Attach the armature plate to the door using appropriate hardware, ensuring it remains flush against the electromagnet when the door is closed.
2. Connecting to the Power Supply
Selecting the Power Supply:
- Choose a power supply that matches the EML’s voltage requirements (12V or 24V DC).
- For most security systems, 12V is standard, but 24V may be preferred for longer wiring runs to reduce voltage drop.
Wiring:
- Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to the positive input on the EML.
- Connect the ground (negative) terminal of the power supply to the ground connection of the system.
3. Integrating the Exit Button
Wiring the Exit Button:
- Connect one terminal of the exit button to the controller’s exit input.
- Connect the other terminal of the exit button to the ground.
Functionality:
- Pressing the exit button sends a signal to the controller to deactivate the EML, allowing the door to open.
4. Connecting to the Controller
Controller Installation:
- Install the controller (e.g., Z-5R for standalone systems or S2000-2 for networked systems) in a secure location near the EML.
Wiring:
- Connect the EML’s control wires to the controller’s output terminals.
- Ensure all connections are secure and protected against tampering.
Relay Integration (if using an Intercom Panel):
- If integrating with an intercom panel that sends an electrical impulse to unlock, install a relay between the panel and the EML.
- Connect the relay’s input to the panel’s relay output and the relay’s output to the EML’s control input.
5. Finalizing the Installation
Testing:
- Power on the system and test the EML by sending unlock commands through the controller.
- Verify that the exit button effectively deactivates the EML, allowing the door to open.
Adjustments:
- Make necessary adjustments to the alignment of the EML and armature plate to ensure smooth operation.
- Ensure all wiring is concealed and secured to prevent interference or tampering.
Best Practices for Electromagnetic Lock Connections
Professional Installation:
- While some installations can be DIY, hiring a certified security professional ensures precise alignment and adherence to safety standards.
Use Quality Components:
- Invest in reputable brands for EMLs, power supplies, controllers, and wiring to ensure reliability and longevity.
Implement Backup Power:
- Use Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) or battery backups to maintain EML functionality during power outages, especially for high-security environments.
Secure Wiring:
- Route cables through concealed pathways such as walls or conduits to protect against tampering and maintain aesthetic appeal.
Regular Maintenance:
- Periodically inspect the EML, power supply, and controller for signs of wear, alignment issues, or electrical problems.
- Clean and lubricate mechanical parts to ensure smooth operation.
Compliance Adherence:
- Follow all relevant electrical codes and standards (e.g., NEC, NFPA) during installation to ensure safety and legal compliance.
Code Management:
- Regularly update access codes and manage user permissions through the controller to maintain security integrity.
Integration with Security Systems:
- Combine EMLs with other security measures such as surveillance cameras, alarm systems, and motion detectors for comprehensive protection.
Protect Against Electrical Surges:
- Use surge protectors and proper grounding to safeguard electrical components from voltage spikes.
User Training:
- Educate authorized users on proper usage and management of the ACMS to maintain system integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
Reputable Brands and Models
Choosing reliable and well-regarded brands ensures the longevity and performance of your electromagnetic locks. Below are some trusted manufacturers and their popular models:
1. BBP
- Overview: Known for producing reliable and cost-effective power solutions tailored for security systems.
- Popular Models:
- BBP EM120: A versatile power supply suitable for small to medium-sized EML installations.
- BBP EM300: Designed for higher security applications requiring robust power delivery.
2. Rapan
- Overview: Offers high-quality power supplies with robust performance and durability.
- Popular Models:
- Rapan PowerPlus 12V: Efficient power supply with built-in surge protection.
- Rapan Secure24 24V: Ideal for long-distance wiring applications with minimal voltage drop.
3. Reserv
- Overview: Specializes in backup power solutions, ensuring continuous operation during outages.
- Popular Models:
- Reserv Backup300: Provides reliable backup power for critical EML systems.
- Reserv UltraBattery 24V: High-capacity battery backup for extended power outages.
4. Bastion ("Skat")
- Overview: Renowned for high-performance and trusted power solutions in the security industry.
- Popular Models:
- Bastion PowerMaster 12V: Premium power supply with advanced protection features.
- Bastion SecureFlow 24V: High-efficiency power supply designed for large-scale EML installations.
5. Z-5R and S2000-2 Controllers
Z-5R Controller:
- Overview: Ideal for standalone ACMS, providing reliable management of EMLs and access devices.
- Features: Supports multiple access methods, easy programming, and robust performance.
S2000-2 Controller:
- Overview: Suitable for networked ACMS, allowing centralized control and monitoring of multiple EMLs.
- Features: Advanced integration capabilities, scalable architecture, and comprehensive management software.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Ensuring that your electromagnetic locks and their power supplies comply with relevant standards is essential for safety, reliability, and legal adherence.
Relevant Standards
NFPA 72 - National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code:
- Governs the design, installation, and maintenance of fire alarm and signaling systems, including aspects related to ACMS integration.
National Electrical Code (NEC):
- Regulates the electrical aspects of alarm system installations to ensure safety and compliance.
UL Standards:
- Provide safety and performance requirements for security alarm devices and components.
OSHA Standards (29 CFR 1910):
- Include fire safety regulations for workplaces, covering the installation and maintenance of fire alarm systems to protect employees.
Local Building Codes:
- Additional requirements specific to your locality must also be adhered to for compliance and safety.
Key Compliance Points
Power Supply Design:
- Ensure all power supplies meet the electrical requirements outlined in NEC and UL standards, including proper grounding and protection mechanisms.
Cable Management:
- Adhere to guidelines for cable routing, minimizing exposure and protecting against physical damage or tampering.
System Integration:
- Ensure that all ACMS components are correctly integrated with other security and safety systems for coordinated operation.
Data Protection:
- Comply with data privacy laws such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) to protect biometric and other sensitive data.
Emergency Power Solutions:
- Implement backup power systems (e.g., UPS, batteries) in compliance with NFPA 72 to ensure system functionality during emergencies.
Final Thoughts
Electromagnetic Locks are essential for creating secure and reliable Access Control and Management Systems (ACMS). Proper connection and integration of these locks with power supplies, controllers, and other security components are crucial to ensure their effective operation and longevity. By understanding the connection schematics, selecting appropriate components, following best installation practices, and adhering to relevant standards, you can enhance the security of your premises significantly. Regular maintenance and system updates further ensure that your electromagnetic locks continue to provide robust protection against unauthorized access.
Key Takeaways:
Choose the Right Voltage: Assess whether 12V or 24V electromagnetic locks are more suitable for your installation based on power consumption and wiring distance.
Select an Adequate Power Supply: Ensure the power supply meets or exceeds the total current requirements of all connected locks and consider future expansions.
Implement Backup Power Solutions: Use UPS or battery backups to maintain lock functionality during power outages, especially for high-security applications.
Ensure Proper Installation: Follow best practices for mounting, wiring, and configuring electromagnetic locks to achieve optimal performance and security.
Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine inspections and maintenance to prevent wear and ensure reliable operation of both locks and power supplies.
Protect Against Electrical Surges: Utilize surge protectors and proper grounding to safeguard electrical components from voltage spikes.
Secure Power Supply Placement: Install power supplies in secure locations to prevent tampering and unauthorized access.
Integrate with Comprehensive Security Systems: Combine electromagnetic locks with other security measures like surveillance cameras and alarm systems for enhanced protection.
Adhere to Standards: Ensure all installations comply with relevant electrical and building codes to guarantee safety and legal compliance.
Professional Assistance: Consider hiring certified security professionals for installation and maintenance to ensure electromagnetic locks operate effectively and securely.
For expert assistance in selecting and installing power supplies for electromagnetic locks, ensuring compliance with relevant standards, or accessing comprehensive project documentation, visit safsale.com. Our specialists are ready to help you design and deploy reliable, compliant, and efficient access control solutions tailored to your specific security needs.
Important Notice on Standards
All referenced documents and standards in this guide are provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as official publications. For authoritative guidelines and legal requirements, always consult the official standards organizations or regulatory bodies.