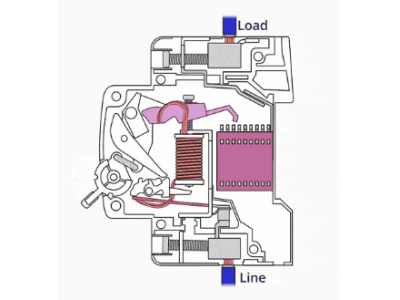
Electrical Protection Devices: Types, Features, and Top Manufacturers
Introduction to Electrical Protection Devices
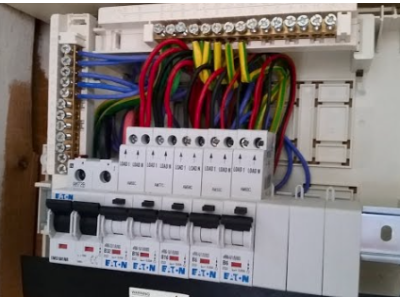
Ensuring the safety and reliability of your home's electrical system is paramount. Electrical protection devices, commonly referred to as "automats," play a crucial role in safeguarding your property and loved ones from electrical hazards. These devices are designed to monitor and control the electrical flow within your network, automatically disconnecting the power in the event of irregularities such as overloads, short circuits, and current leaks. At safsale.com, we offer a wide range of high-quality electrical protection devices to meet your safety and performance needs.
Importance of Electrical Protection
Electrical networks can operate under both normal and abnormal conditions. Abnormal conditions include:
- Overloads: Excessive current flowing through the system.
- Short Circuits: Direct connections between live conductors.
- Current Leaks: Unintended paths for electrical current, leading to potential shocks.
- Voltage Surges: Sudden increases in voltage that can damage appliances and wiring.
Failure to protect against these conditions can result in damaged wiring, malfunctioning electrical appliances, fire hazards, and even electrocution. Electrical protection devices are essential in mitigating these risks, ensuring a safe and efficient electrical system.
Types of Electrical Protection Devices
Electrical protection devices can be categorized based on their purpose and operating principles. The main types include:
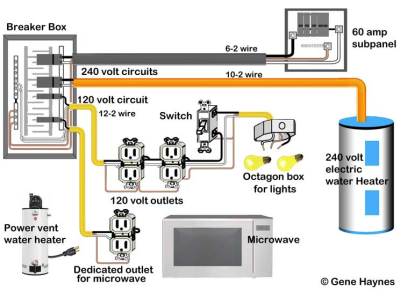
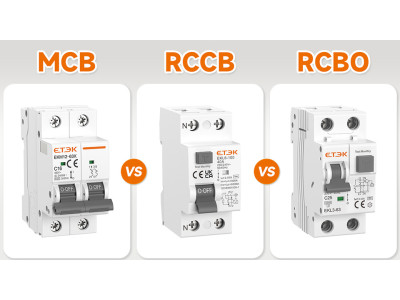
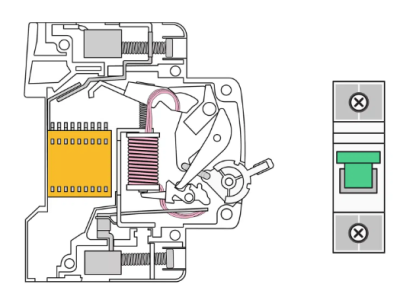
1. Automatic Circuit Breakers
Automatic circuit breakers are fundamental components of any electrical protection system. They are designed to automatically disconnect the electrical circuit when they detect an overload or short circuit.
Types of Automatic Circuit Breakers:
- Thermal Breakers: Utilize a bimetallic strip that bends when heated by excess current, triggering the breaker to trip.
- Magnetic Breakers: Use an electromagnet that activates rapidly in the event of a short circuit, providing immediate disconnection.
Features:
- Adjustable Settings: Allows customization of the trip threshold based on the specific needs of the circuit.
- Reset Capability: Can be easily reset after tripping without the need for replacement.
Advantages:
- Protection: Safeguards against electrical fires and equipment damage.
- Convenience: Easily resettable after tripping, reducing downtime.
Applications:
- Residential homes
- Commercial buildings
- Industrial facilities
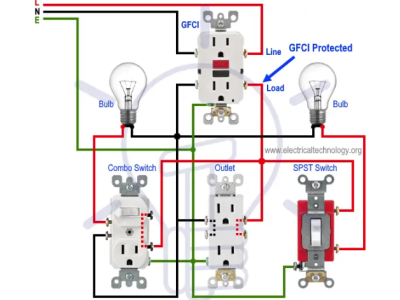
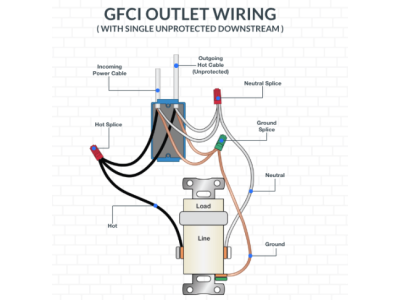
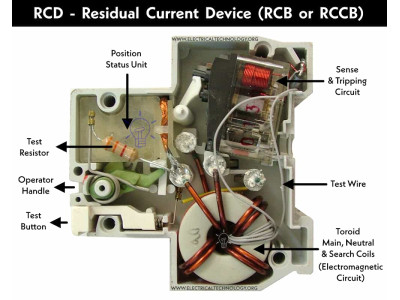
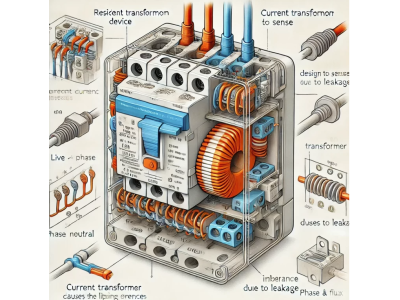
2. Residual Current Devices (RCDs)
Residual Current Devices (RCDs), also known as Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs), detect imbalances between the incoming and outgoing current, indicating a potential current leak.
Functionality:
- Detection: Monitors the current flow in the live and neutral wires.
- Tripping Mechanism: Disconnects the circuit if a difference (typically above 10 mA) is detected, preventing electric shocks.
Features:
- Sensitivity: High sensitivity to small current leaks.
- Fast Response Time: Quickly interrupts the circuit to enhance safety.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Safety: Protects against electric shocks and electrocution.
- Fire Prevention: Reduces the risk of electrical fires caused by current leaks.
Applications:
- Bathrooms and kitchens
- Outdoor outlets
- High-risk areas requiring enhanced protection
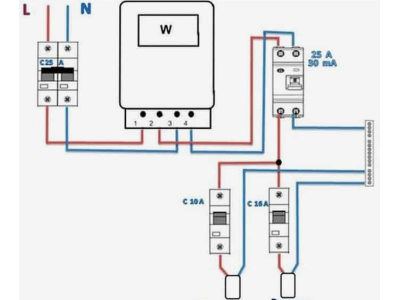
3. Differential Circuit Breakers
Differential Circuit Breakers, or Differential Automats, combine the functionalities of both RCDs and automatic circuit breakers within a single unit.
Features:
- Integrated Protection: Provides both overload and current leak protection.
- Space Efficiency: Combines two protective mechanisms in one device, saving space in the electrical panel.
Advantages:
- Comprehensive Protection: Offers complete safeguarding against both overcurrents and earth faults.
- Cost-Effective: Eliminates the need for separate RCDs and circuit breakers.
Applications:
- Residential electrical panels
- Commercial buildings
- Industrial settings requiring robust protection
4. Voltage Relays
Voltage Relays are specialized devices that protect electrical equipment from voltage fluctuations by disconnecting the power supply when voltage exceeds or drops below predefined limits.
Functionality:
- Monitoring: Continuously monitors the voltage levels within the electrical network.
- Protection Mechanism: Trips the circuit if voltage anomalies are detected, preventing damage to appliances and wiring.
Features:
- Adjustable Thresholds: Allows customization of voltage limits based on equipment requirements.
- Multiple Voltage Points: Capable of protecting against both overvoltage and undervoltage conditions.
Advantages:
- Equipment Protection: Safeguards sensitive electrical devices from voltage-induced damage.
- System Stability: Maintains consistent voltage levels, enhancing overall electrical system performance.
Applications:
- Home electronics and appliances
- Industrial machinery
- Commercial electrical systems
Key Features and Characteristics of Electrical Protection Devices
When selecting electrical protection devices, consider the following key parameters to ensure optimal performance and safety:
1. Performance (Air Exchange Capacity)
Performance measures the device's ability to handle electrical currents safely. For example, an automatic circuit breaker with a rating of 6 kW is suitable for standard residential doorways measuring 800*2000 mm, ensuring effective protection.
2. Power Consumption
Electrical protection devices vary in power requirements. For instance, devices operating in rooms with ceiling heights up to 3 meters and areas of 10 m² typically require around 1 kW of electrical power.
3. Noise Level
Some protection devices, especially those with motors and fans, can generate significant noise. Models operating below 30 dB are considered quiet and suitable for residential use, while louder models may be better suited for industrial environments.
4. Airflow Direction
The direction of the air stream, whether vertical or horizontal, depends on the installation type. Proper orientation is crucial to avoid reduced device lifespan and ensure effective performance.
5. Temperature Range
Most electrical protection devices are designed to operate within a temperature range of -20°C to +40°C, making them suitable for various climates and indoor conditions.
6. Physical Dimensions
The size of the device should match the dimensions of the installation area to ensure complete coverage and avoid dead zones that can compromise protection efficacy.
Choosing the Right Electrical Protection Device
Selecting the appropriate electrical protection device involves evaluating several factors to ensure it meets your specific safety and performance needs:
1. Boiler Type and Capacity
- Gas Boilers: Require devices that can supply adequate oxygen for combustion and remove exhaust gases efficiently.
- Electric Boilers: While they do not produce combustion gases, protection devices are still necessary to manage electrical loads and prevent overcurrents.
2. Room Size and Layout
- Calculation: Determine the volume of the electrical network to select devices with appropriate current ratings and protection capacities.
- Distribution: Ensure even distribution of protection devices to cover all areas of the electrical system.
3. Climate Considerations
- Cold Climates: Devices with enhanced durability and protection against voltage drops and surges caused by extreme temperatures.
- Humid Regions: Protection against corrosion and moisture-related electrical faults.
4. Energy Efficiency
- High SEER Ratings: Choose devices with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratios to minimize energy consumption.
- Smart Controls: Devices with programmable settings and remote management capabilities offer enhanced efficiency and convenience.
5. Budget
- Cost vs. Features: Balance initial investment with long-term operational savings and required safety features.
- Quality vs. Price: Opt for reputable brands that offer reliable performance and durability, even if they come at a higher price point.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Electrical Protection Devices
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of electrical protection devices. Regular upkeep helps prevent system failures and ensures continuous protection.
Key Maintenance Tasks
Regular Inspection
- Visual Checks: Inspect devices for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Functional Testing: Periodically test the trip mechanisms to ensure they operate correctly.
Cleaning
- Dust Removal: Keep devices free from dust and debris that can impede functionality.
- Filter Maintenance: For devices with filters, clean or replace them as per manufacturer recommendations.
Component Checks
- Wiring: Ensure all connections are secure and free from fraying or damage.
- Mechanical Parts: Lubricate moving parts if necessary and check for smooth operation.
System Testing
- Load Testing: Verify that devices trip at their rated current levels to ensure proper protection.
- Leak Testing: For RCDs, test for sensitivity to ensure they trip at the correct leakage current.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Insufficient Airflow or Trip Issues
- Causes: Overloaded circuits, faulty devices, or poor connections.
- Solutions: Reduce the electrical load, replace defective devices, and secure all connections.
Excessive Noise
- Causes: Loose components, debris in mechanical parts, or failing motors.
- Solutions: Tighten any loose parts, clean mechanical components, and replace malfunctioning motors.
Unpleasant Odors or Smoke
- Causes: Overheating components, electrical shorts, or burning insulation.
- Solutions: Immediately disconnect power, inspect for faults, and replace damaged parts.
Non-Responsive Devices
- Causes: Power supply issues, faulty switches, or internal damage.
- Solutions: Check power connections, reset breakers, and replace damaged devices as necessary.
Leading Manufacturers and Brands
Several reputable brands dominate the electrical protection device market, offering reliable and high-performance products tailored to various needs:
- Siemens: Renowned for their advanced technology and robust protection devices suitable for both residential and industrial applications.
- Schneider Electric: Offers a wide range of electrical protection solutions known for their reliability and innovation.
- Leviton: Known for their user-friendly and efficient circuit breakers and RCDs.
- ABB: Provides high-quality protection devices with a focus on energy efficiency and safety.
- Eaton: Specializes in comprehensive electrical management solutions, including advanced protection devices.
- Hager: Offers reliable and cost-effective electrical protection devices tailored for home and commercial use.
Each manufacturer provides unique features and benefits, allowing consumers to select devices that best meet their specific safety and performance requirements.
Conclusion
Electrical protection devices are indispensable for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system in homes, apartments, and cottages across the USA. By understanding the different types of devices-automatic circuit breakers, RCDs, differential circuit breakers, and voltage relays-homeowners can make informed decisions to enhance electrical safety and prevent potential hazards. Regular maintenance and adherence to safety standards further ensure the reliability and longevity of these critical components.
At safsale.com, we offer a comprehensive selection of top-quality electrical protection devices from leading manufacturers. Equip your home with the best protection solutions to safeguard your electrical network, ensuring peace of mind and a safe living environment for your family.
For more information and to explore our range of electrical protection devices, visit safsale.com