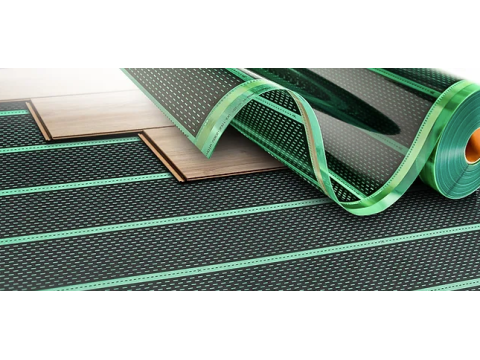
Infrared film heated floors are an emerging technology in electric heating, gaining trust and popularity among homeowners for their reliability, safety, and efficiency. By integrating thin, non-conductive films embedded with infrared heating elements beneath the floor surface, these systems provide a comfortable and evenly distributed heat source. This guide delves into the principles of infrared film heated floors, their advantages and disadvantages, installation procedures, compatible flooring types, and best practices to help you make an informed decision for your home or apartment.
What Are Infrared Film Heated Floors?
Infrared film heated floors consist of thin, non-conductive films, typically ranging from 1.5 to 3 mm in thickness, embedded with ultra-fine carbon fibers that generate heat when electrical current passes through them. These systems operate at low temperatures, typically maintaining water temperatures between 35°C and 45°C (95°F to 113°F), ensuring high efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Key Components of Infrared Film Heated Floors:
Infrared Heating Film:
- Construction: Composed of dielectric (non-conductive) films with embedded carbon heating elements.
- Durability: High tensile strength ensures reliability and safety during operation.
Insulation Layers:
- Reflective Foil: Enhances heat distribution by reflecting infrared radiation upwards.
- Thermal Insulation: Prevents heat loss downward, ensuring efficient heating of the living space.
Control Systems:
- Thermostats: Allow precise temperature control and scheduling for optimal comfort and energy savings.
- Smart Controls: Integration with smart home systems for remote management and automation.
Flooring Materials:
- Tile and Stone: High thermal conductivity materials ideal for radiant heating.
- Laminate and Vinyl: Compatible with infrared heated floors but may require additional insulation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Infrared Film Heated Floors
Advantages
Versatility:
- Universal Installation: Compatible with various flooring types, including tile, vinyl, laminate, and carpet.
- Flexibility in Placement: Can be installed across entire floor areas or localized zones, such as near beds or seating areas.
Ease of Installation:
- Dry Installation: Typically installed on a dry floor surface without the need for concrete screed, making the process quicker and less labor-intensive.
- DIY-Friendly: Lightweight and easy to handle, allowing for potential DIY installations with minimal expertise.
Energy Efficiency:
- Low Power Consumption: Operates efficiently at low temperatures, reducing energy usage by 20-40% compared to traditional electric cable systems.
- Quick Heating: Rapidly heats the floor surface, providing immediate warmth and reducing overall heating time.
Comfort and Aesthetics:
- Even Heat Distribution: Provides consistent and comfortable warmth from the floor upwards, enhancing the overall living environment.
- Invisible Heating: No visible heating units or radiators, preserving the aesthetic integrity of interiors and allowing flexible furniture arrangement.
Safety and Reliability:
- Low Temperature Operation: Reduces the risk of burns and overheating, making it safe for households with children and pets.
- Durable Construction: High-strength dielectric films and carbon elements ensure long-term reliability and performance.
Disadvantages
Higher Energy Costs:
- Electricity Dependence: As an electric heating system, infrared film heated floors can lead to higher electricity bills, especially in areas with elevated energy rates.
- Operational Expenses: Continuous use without proper control can result in significant energy consumption.
Installation Limitations:
- Electrical Load: Requires adequate electrical capacity and proper wiring to handle the heating system, which may necessitate electrical system upgrades.
- Flooring Restrictions: Not suitable for all flooring types, particularly those that may degrade or damage the heating film under heavy use or sharp objects.
Maintenance and Longevity:
- Potential for Damage: While durable, the heating film can be susceptible to damage from heavy furniture placement or accidental punctures.
- Limited Lifespan: Over time, the carbon elements may degrade, reducing heating efficiency and necessitating replacement.
Temperature Control Challenges:
- Manual Adjustments: Basic models without electronic controls may require manual adjustments to maintain desired temperatures, leading to inconsistent heating.
- Thermostat Placement: Incorrect placement of thermostats can result in inaccurate temperature readings and inefficient heating.
Applications of Infrared Film Heated Floors
Infrared film heated floors are versatile and can be effectively utilized in various settings, offering both primary and supplementary heating options.
1. Infrared Film Heated Floors in Apartments
Considerations
- Space Constraints: Apartments often have limited space, making the compact and flexible design of infrared film heated floors ideal.
- Electrical Capacity: Assess the apartment’s electrical infrastructure to ensure it can support the heating system’s power requirements.
- Hot Water Integration: If combined with other heating systems, ensure seamless integration for comprehensive heating solutions.
Recommendations
- Radiant Heating Areas: Ideal for areas where people spend a lot of time standing, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and entryways.
- Supplementary Heating: Can be used alongside existing heating systems to provide targeted warmth and improve overall comfort.
- Zoning: Implement zoning to control heating in different areas independently, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing costs.
2. Infrared Film Heated Floors in Private Homes
Considerations
- Hot Water Demand: Private homes typically have higher and more varied hot water needs, requiring scalable heating solutions.
- Energy Efficiency: Balancing initial costs with long-term energy savings is essential for cost-effective heating.
- Installation Flexibility: Private homes offer more flexibility in terms of installation locations and system configurations.
Recommendations
- Whole-Home Heating: Suitable for entire floor areas in homes, providing consistent and comfortable warmth throughout living spaces.
- Custom Zoning: Implement zoning to control heating in different areas independently, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort.
- Integration with Smart Home Systems: Incorporate smart controls for remote management and automation, optimizing energy usage based on occupancy and preferences.
Types of Floor Coverings Compatible with Infrared Film Heated Floors
Choosing the right flooring material is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and longevity of infrared film heated floors. The most compatible and effective flooring types include:
1. Tile Flooring
Advantages:
- High Thermal Conductivity: Efficiently transfers heat from the infrared film to the room, ensuring effective heating.
- Durability: Resistant to moisture and wear, making it ideal for high-traffic areas like kitchens and bathrooms.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Wide variety of styles and finishes available to complement any interior design.
Installation Tips:
- Ensure the heating film is properly secured and evenly distributed beneath the tile to prevent cold spots.
- Use appropriate thin-set mortars that allow for effective heat transfer.
2. Vinyl Flooring
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Easily accommodates the installation of infrared film heated floors without the risk of cracking.
- Variety: Available in numerous patterns and colors to match any décor.
- Water Resistance: Suitable for areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
Installation Tips:
- Choose vinyl planks or sheets with high thermal conductivity for optimal heat transfer.
- Ensure proper sealing around edges and fixtures to prevent heat loss.
3. Laminate Flooring
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Offers a budget-friendly alternative to more expensive flooring options while still providing a stylish appearance.
- Easy Installation: Click-lock designs make installation straightforward, even for DIY enthusiasts.
- Durability: Resistant to scratches and wear, suitable for high-traffic areas.
Installation Tips:
- Select laminate flooring with a thermal rating compatible with infrared heating systems.
- Install a suitable underlayment that allows for efficient heat transfer and insulation.
4. Carpet Flooring
Considerations:
- Insulation Properties: Carpets can insulate the floor, reducing heat transfer efficiency.
- Compatibility: Not typically recommended for infrared film heated floors unless paired with low-pile, breathable carpets designed for radiant heating.
Installation Tips:
- Use carpets with low thermal resistance to ensure effective heat transfer.
- Avoid heavy or plush carpets that can trap heat and reduce system efficiency.
5. Wood Flooring (Parquet)
Considerations:
- Thermal Sensitivity: Frequent temperature changes can cause wood to expand and contract, potentially leading to warping or damage.
- Not Recommended: Generally not advised for use with infrared film heated floors due to the risk of structural issues over time.
Installation and Mounting of Infrared Film Heated Floors
Proper installation of infrared film heated floors is essential to ensure efficient performance, safety, and longevity. The process typically involves preparing the base, laying the heating film, installing insulation, and finishing with the final flooring material.
1. Installation Methods
Dry Installation:
- Description: The heating film is laid directly onto a dry, level floor surface without the need for concrete screed.
- Advantages: Faster and less labor-intensive compared to wet installation methods, suitable for existing homes and retrofit projects.
- Disadvantages: May require additional protective layers to safeguard the heating film from heavy furniture and foot traffic.
2. General Installation Guidelines
Preparation and Leveling of the Base:
- Ensure the floor surface is clean, dry, and level.
- Remove any existing flooring materials if necessary and repair any imperfections.
Laying and Connecting the Heating Film:
- Roll out the infrared heating film parallel to the longest wall for optimal heat distribution.
- Cut the film to fit the room dimensions, ensuring minimal waste and seamless coverage.
- Secure the heating film using manufacturer-recommended adhesives or tapes to prevent movement during installation.
Installing Insulation Layers:
- Place a reflective foil insulation layer over the heating film to enhance heat reflection and prevent heat loss downward.
- Ensure the insulation is smooth and free of wrinkles to maintain effective heat transfer.
Final Flooring Installation:
- Install the chosen flooring material over the heating system, following manufacturer guidelines to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
- Use appropriate adhesives or fastening methods to secure the flooring without damaging the heating film.
Electrical Connection and Control Integration:
- Connect the heating film to the electrical supply through a dedicated circuit, adhering to local electrical codes.
- Install and program the thermostat or smart control system to manage the heating schedule and temperature settings.
3. Mounting Considerations for Different Flooring Materials
1. Tile Flooring
- Installation:
- Use a wet installation method with concrete screed for maximum stability and heat efficiency.
- Ensure the heating film is embedded evenly within the screed to prevent cold spots.
2. Laminate Flooring
- Installation:
- Typically installed using a dry method, laying the heating film directly beneath the laminate planks.
- Use a suitable underlayment that allows for efficient heat transfer and insulation.
3. Vinyl Flooring
- Installation:
- Can be installed using a dry method, laying the heating film directly beneath the vinyl sheets or planks.
- Ensure proper sealing around edges and fixtures to prevent heat loss.
4. Carpet Flooring
- Installation:
- Use low-pile, breathable carpets to ensure effective heat transfer.
- Avoid placing heavy furniture directly on the heating film to prevent damage and ensure efficient operation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Infrared Film Heated Floors
Advantages
Energy Efficiency:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Operates efficiently at low temperatures, minimizing energy usage by 20-40% compared to traditional electric cable systems.
- On-Demand Heating: Heats only the occupied areas, reducing standby energy losses and lowering utility bills.
Comfort and Aesthetics:
- Even Heat Distribution: Provides consistent and comfortable warmth from the floor upwards, enhancing the overall living environment.
- Invisible Heating: No visible heating units or radiators, preserving the aesthetic integrity of interiors and allowing flexible furniture arrangement.
Safety and Reliability:
- Low Temperature Operation: Reduces the risk of burns and overheating, making it safe for households with children and pets.
- Durable Construction: High-strength dielectric films and carbon elements ensure long-term reliability and performance.
Ease of Installation:
- Dry Installation: Faster and less labor-intensive compared to wet installation methods, suitable for existing homes and retrofit projects.
- Lightweight: Easy to handle and install, potentially allowing for DIY installations with minimal expertise.
Environmental Benefits:
- Lower Carbon Footprint: More efficient use of electricity can lower overall energy consumption and carbon emissions, especially when paired with renewable energy sources.
Disadvantages
Higher Energy Costs:
- Electricity Dependence: As an electric heating system, infrared film heated floors can lead to higher electricity bills, especially in areas with elevated energy rates.
- Operational Expenses: Continuous use without proper control can result in significant energy consumption.
Installation Limitations:
- Electrical Load: Requires adequate electrical capacity and proper wiring to handle the heating system, which may necessitate electrical system upgrades.
- Flooring Restrictions: Not suitable for all flooring types, particularly those that may degrade or damage the heating film under heavy use or sharp objects.
Maintenance and Longevity:
- Potential for Damage: While durable, the heating film can be susceptible to damage from heavy furniture placement or accidental punctures.
- Limited Lifespan: Over time, the carbon elements may degrade, reducing heating efficiency and necessitating replacement.
Temperature Control Challenges:
- Manual Adjustments: Basic models without electronic controls may require manual adjustments to maintain desired temperatures, leading to inconsistent heating.
- Thermostat Placement: Incorrect placement of thermostats can result in inaccurate temperature readings and inefficient heating.
Best Practices for Implementing Infrared Film Heated Floors
Implementing infrared film heated floors effectively involves strategic planning, careful selection of components, and ongoing management to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
1. Strategic Placement and Zoning
- High-Traffic Areas: Focus heating in areas where people spend the most time, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and living rooms.
- Zoning: Divide the home into different heating zones to control temperature independently, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing costs.
2. Optimize Control Settings
- Thermostat Configuration: Properly set thermostats to avoid overheating, reducing energy consumption.
- Smart Controls: Utilize smart thermostats and remote controls to manage heating schedules, monitor energy usage, and adjust settings based on occupancy and preferences.
3. Enhance Home Insulation
- Floor Insulation: Install high-quality insulation beneath the heating film to minimize heat loss downward, increasing system efficiency.
- Wall and Ceiling Insulation: Improve overall home insulation to maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduce the heating load on the infrared heated floors.
4. Choose Compatible Flooring Materials
- High Thermal Conductivity: Opt for flooring materials with high thermal conductivity, such as tile or stone, to ensure effective heat transfer.
- Thickness Considerations: Choose thinner flooring materials or ensure adequate spacing between heating elements and the floor surface to maximize heating efficiency.
5. Regular Maintenance and Inspection
- Routine Checks: Periodically inspect the heating system for any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction to address issues proactively.
- Descaling: Clean and descale the system as needed to maintain heating efficiency and prevent damage, especially in areas with hard water.
6. Professional Installation and Compliance
- Licensed Professionals: Engage licensed electricians and flooring specialists to ensure proper installation, adherence to safety standards, and compliance with local building codes.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions meticulously to maintain warranty coverage and ensure optimal system performance.
7. Energy-Efficient Practices
- Low-Flow Fixtures: Install low-flow faucets and showerheads to reduce hot water consumption without sacrificing performance.
- Renewable Integration: Pair infrared film heated floors with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to offset electricity usage and enhance sustainability.
8. User Education and Training
- Operating Instructions: Educate household members on how to use and manage the heating system effectively, including setting thermostats and understanding control features.
- Safety Practices: Ensure that users are aware of safety precautions, such as avoiding placing heavy furniture directly on heating films to prevent damage.
Conclusion
Infrared film heated floors offer a modern and efficient solution for providing consistent and comfortable warmth in both apartments and private homes. With their energy efficiency, ease of installation, and aesthetic advantages, they enhance the living experience by creating a cozy and inviting environment. While infrared film heated floors come with certain challenges, such as higher energy costs and potential installation limitations, their numerous benefits make them a valuable addition to contemporary living spaces.
By understanding the different types of infrared film heated floors, evaluating your household’s specific needs, and implementing energy-efficient practices, you can achieve a reliable and cost-effective heating solution. Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to maximize the benefits and ensure the longevity of your infrared film heated floor system.
Key Takeaways:
Understand Heating Types: Familiarize yourself with infrared film heated floors to choose the right fit for your home.
Assess Household Needs: Evaluate hot water demand, household size, and usage patterns to determine the appropriate capacity and type.
Prioritize Energy Efficiency: Implement strategies like proper thermostat settings, zoning, and enhancing home insulation to maximize energy efficiency.
Choose Compatible Flooring: Select flooring materials with high thermal conductivity to ensure effective heat transfer and optimal system performance.
Regular Maintenance: Keep your heating system well-maintained through regular inspections, descaling, and timely repairs to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Leverage Smart Technology: Utilize smart thermostats and remote controls for enhanced management, automation, and energy savings.
Seek Professional Assistance: Engage licensed electricians and flooring specialists for installation and maintenance to ensure compliance with safety standards and optimal system functionality.
Balance Costs and Benefits: Weigh the higher initial investment against the long-term energy savings and comfort benefits of infrared film heated floors.
Integrate Renewable Energy: Explore integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels to offset operational costs and promote sustainability.
Stay Informed: Keep up with advancements in heating technologies to continuously improve and upgrade your system for better performance and efficiency.
For expert assistance in selecting and installing infrared film heated floors, ensuring compatibility with your home’s infrastructure, or accessing comprehensive project documentation, visit safsale.com. Our specialists are ready to help you create a reliable, efficient, and comfortable living environment tailored to your specific needs.
Important Notice on Standards
All referenced documents and standards in this guide are provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as official publications. For authoritative guidelines and legal requirements, always consult the official standards organizations or regulatory bodies.