A motion sensor is an electronic device that detects the presence or movement of objects within a designated area. By registering changes in physical parameters-like heat, sound waves, or electromagnetic fields-it provides real-time activation signals for alarms, lights, or other automated systems. Below, we discuss why these sensors matter, how they operate, installation considerations, and their advantages for both home and business environments.
1. Why Motion Sensors Matter
Motion sensors serve numerous purposes:
- Security: As a critical part of security systems, sensors detect unauthorized entry and trigger alarms or surveillance recording.
- Automatic Lighting: By switching lights on only when occupants are present, sensors conserve energy and lower utility costs.
- Building Automation: In “smart home” and commercial settings, they coordinate HVAC systems, door access, and more, adapting to real-time occupancy patterns.
2. How Motion Sensors Work
Modern motion sensors generally use three principal detection technologies:
2.1 Passive Infrared (PIR)
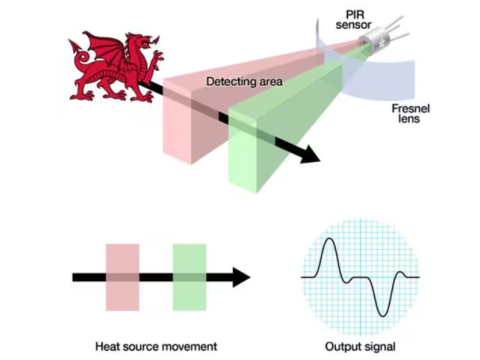
PIR sensors detect changes in infrared (heat) radiation in their field of view. Humans, animals, and other warm objects emit IR radiation distinct from the ambient environment. When a moving warm object enters the sensor’s detection zone, the PIR element registers a thermal shift and triggers an output.
- Pros:
- Affordable, reliable, and widespread in consumer devices
- Insensitive to static heat sources (like stationary radiators)
- Cons:
- Limited range and angle coverage relative to some other technologies
- Potential false alarms caused by abrupt temperature changes or direct airflow
2.2 Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves (above human hearing) and analyze reflected echoes. Movement alters how these echoes return to the receiver, indicating motion is present.
- Pros:
- Effective in humid environments
- Detects soft objects that may not emit heat
- Cons:
- Risk of false alarms from loud, high-frequency noises or mechanical vibrations
- Shorter detection range compared to microwave sensors
2.3 Microwave
Microwave sensors transmit low-power radio waves and interpret Doppler shifts in frequency upon reflection from moving objects.
- Pros:
- Can penetrate thin walls or non-metallic barriers
- More stable performance against air drafts or temperature shifts
- Cons:
- Potential false triggers if movement occurs behind walls
- Generally more expensive than PIR or ultrasonic options
Most residential and commercial lighting controls use PIR sensors due to their reliability, affordability, and straightforward coverage needs.
3. Common Applications
-
Security Systems:
- Detect intrusion or suspicious movement around a property
- Work day and night, with minimal human oversight
- Often combined with cameras to record only on motion detection
-
Automatic Lighting:
- Corridors, hallways, stairwells, and sporadically used rooms
- Reduces energy usage by turning off lights when not needed
- Adjustable time delays and ambient light thresholds for optimal efficiency
-
Building Automation (Smart Home):
- Triggers HVAC adjustments or partial lighting when occupants enter rooms
- Integrates with larger control networks to run complex scenes or schedules (e.g., night mode or away mode)
4. Installation and Setup
4.1 Placement Strategy
- Coverage Area: Align the sensor to oversee the desired zone, avoiding overshoot into adjacent spaces.
- Mounting Height: Typically 7-8 feet (2.1-2.5 m) above the floor. Mount at a slight downward angle for wide coverage.
- Avoid Heat Sources or Direct Sunlight: PIR sensors can be confused by large radiators or sunny windows.
- Distance From HVAC Ducts: Minimizes false triggers from airflow or temperature fluctuations.
4.2 Sensitivity Adjustment
Most motion sensors feature configurable sensitivity:
- High Sensitivity: More prone to false triggers (e.g., small pets, drafts).
- Low Sensitivity: May miss slow or minor motions.
- Pet Immunity Mode: Some designs filter out small animals under a certain weight or size.
Tuning the sensitivity ensures a balance between reliable detection and minimal false alarms.
5. Advantages of Using Motion Sensors
5.1 Energy Efficiency
By activating lights or systems only upon detecting movement, motion sensors significantly lower power consumption. Savings can exceed 30-80% in areas with intermittent occupancy. Light fixtures, in particular, benefit from reduced “on” time-extending bulb lifespans and decreasing maintenance needs.
5.2 Enhanced Security
Motion sensors guard properties continuously:
- Immediate Alerts: Trigger alarms, turn on lights, or activate cameras upon detecting movement.
- Discourages Trespassing: Instant lighting or audible alarms can scare off potential intruders.
- Event-Triggered Recording: In surveillance setups, they reduce file storage by recording only when motion is present.
6. Limitations and Maintenance
Environmental Factors:
- Extreme temperatures, high humidity, or dust can lead to false triggers or hamper performance.
- Electromagnetic interference near large machinery or high-voltage lines might affect some sensor models.
Sensor Cleaning and Testing:
- Lens Cleaning: Particularly for PIR sensors, keep the lens dust-free.
- Periodic Checks: Verify the sensor’s orientation and detection range.
- Updating Settings: Adjust sensitivity as household needs evolve (adding a pet, rearranging furniture, etc.).
Conclusion
Motion sensors play a critical role in modern security and automation, enabling real-time occupant detection for lighting control, alarm systems, and more. By selecting the appropriate detection technology-PIR, ultrasonic, or microwave-installing correctly, and fine-tuning sensitivity, you can achieve reliable performance with minimal false alarms. Combining these sensors with broader automation strategies offers greater efficiency, safety, and comfort.
For tailored advice on choosing and implementing motion sensors for residential or commercial environments, safsale.com provides comprehensive guidance, ensuring you get the right technology for your specific application.