At safsale.com, we know how important it is for the American audience to understand the basics of electricity, especially given the prominence of cutting-edge electrical systems across the USA. Electricity is fundamental to our lives, powering everything from home appliances and HVAC systems to large industrial facilities. Below, we’ll explore a simplified explanation of what electricity is, what an electrical charge means, and how these principles translate into real-world applications. ⚡
Defining Electricity in Simpler Terms
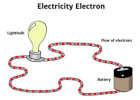
From a scientific standpoint, electricity refers to the set of phenomena arising from the interaction and movement of electrical charges. In more practical terms, it’s the flow of energy we harness to operate countless devices in our daily lives. If you’ve ever flipped a light switch or charged your phone, you’ve directly engaged with electricity.
Electrical Charge is a core concept:
- It’s a fundamental property of certain particles, determining their interaction within electromagnetic fields.
- Charges can be positive or negative, and their movement forms the basis of electrical current.
When we dive deeper into electromagnetic fields, partial derivatives, and advanced equations, the mathematics can become quite complex. At safsale.com, we prefer a more accessible approach for beginners-focusing on real-world uses across the USA while preserving key scientific insights.
Electricity as a Form of Energy
In the realm of physics, energy is the ability to perform work. This work could manifest in multiple ways:
- Mechanical Energy: Turning a turbine or moving a car.
- Thermal Energy: Boiling water or heating a room.
- Electrical Energy: Powering gadgets, lighting, or motors.
Electricity is a type of energy that can be generated from numerous sources. For example:
- Mechanical Energy → Electricity: Via a generator turned by wind or water turbines.
- Chemical Energy → Electricity: Through batteries or fuel cells that rely on electrochemical reactions.
No matter the source, we can transmit electricity via wires (or other mediums) and then convert it on-site into heat, light, or mechanical power. Think of it like a mediator for energy transfer-easy to produce in one location and direct to another.
Seeing Electricity as a “Black Box”
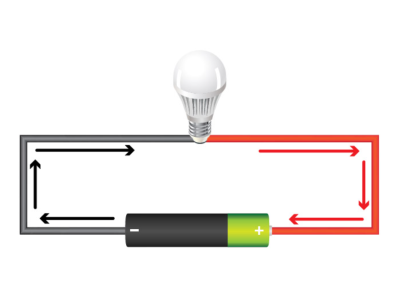
Consider the energy source-the generator or battery-as a “black box.” We don’t need to deep-dive into its internal workings to appreciate what comes out: a specific voltage or electromotive force (EMF), which pushes electrical charges through conductors. By tapping into this EMF, we channel electrical energy to wherever we need it.
For instance:
- Generator in a Hydroelectric Dam: Converts the potential energy of water falling from a higher elevation (in feet rather than meters, per American standards) into electrical power.
- Battery in a Car: Utilizes stored chemical energy to start the engine and run electronic systems.
Once you have an established electrical source, you simply create a path-often copper or aluminum wiring-for the electrons to flow. The system then distributes electricity to equipment or appliances that need it.
Practical Application: The Power Chain
- Power Source (Generator or Battery): This “creates” electricity by converting some form of energy into electrical energy.
- Electrical Network (Wiring, Transmission): Distributes the power over short or long distances.
- End User (Load or Appliance): Converts electrical energy into another form-light, heat, mechanical motion, etc.
In the USA, for example, typical household outlets deliver around 120 volts AC. Many industrial settings use higher voltages-like 480 volts AC-to power heavy machinery. The concept remains the same: electricity travels from the source to the end user. At safsale.com, we emphasize compliance with ASTM and IEEE standards to ensure safe and efficient distribution.
Electricity for Lighting, Heating, and Motors
Lighting:
Turning electrical energy into visible light-commonly via LED lamps or older incandescent bulbs.
Heating:
Using resistance elements to transform electricity into heat (measured in BTUs instead of joules, aligning with American customary units).
Motors:
Converting electricity into mechanical energy, driving everything from small fans to industrial robots.
These versatile applications highlight why electricity is indispensable, especially across the USA, where infrastructure heavily relies on stable power systems.
The Connection Between Electricity and Safety
Because electricity moves charges so effectively, it poses safety risks if handled incorrectly. In the USA, guidelines from organizations like NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulate how we install and operate electrical systems. At safsale.com, we frequently reference these standards to ensure your electrical applications meet the highest safety requirements.
From Scientific Theory to Everyday Life
While advanced physics delves into electric fields, electromagnetic interactions, and advanced partial differential equations, the day-to-day meaning of electricity for the average person in the USA is more tangible:
- Flip a switch → Lights turn on
- Plug in a device → Battery charges or device powers up
- Press a button → Microwave heats your meal
The beauty of electricity is how easily it can be transmitted and converted. Without it, modern civilization as we know it-featuring climate-controlled buildings, 24/7 digital connectivity, and advanced medical devices-would be nearly impossible.
A Quick Look at Future Innovations
Electrical research constantly evolves in the USA, leading to:
- High-Efficiency Solar Panels: Converting more sunlight to electricity.
- Advanced Energy Storage: More powerful batteries for electric vehicles.
- Smart Grids and IoT: Real-time energy management in homes and cities.
These advancements further highlight how crucial electricity is for society. As technology improves, we see even greater reliance on stable and sustainable electrical infrastructures.
Final Thoughts
Electricity is both fundamental and transformative, bridging the gap between raw energy and practical use. It’s the force behind countless devices, an agent of innovation, and a critical part of everyday life, especially in the USA with its massive demand for power in commercial, residential, and industrial sectors.
At safsale.com, we’re committed to explaining these core concepts in a down-to-earth manner-whether you’re curious about installing a simple LED fixture or exploring the intricacies of a high-voltage system. By understanding electricity, you empower yourself to make safer, more efficient decisions about how you generate, distribute, and use this incredible form of energy ⚡.
For more in-depth guidance on electrical systems, safety protocols, and best practices to meet American market demands, visit safsale.com. Together, let’s shed light on the power coursing through our wires-turning raw energy into meaningful progress!
-400x300.jpeg)
