Purpose and Characteristics of Electrical Relays
An electrical relay is a switching device used to close or open an electrical circuit under the influence of certain factors. Depending on what triggers the relay, they can be categorized into different types:
- Electromagnetic Relays
- Thermal Relays
- Photo Relays, and more.
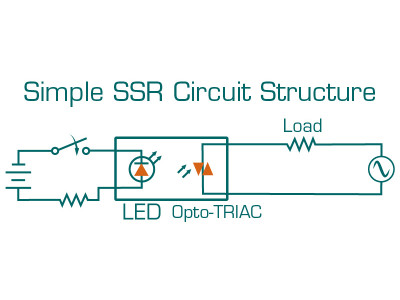
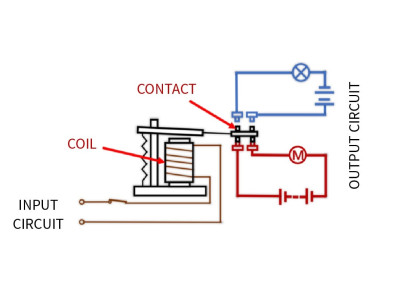
Structurally, a relay consists of a control mechanism and an actuating part. The actuating part typically includes mechanical contact groups, although solid-state relays operate with semiconductor elements to switch voltage and current.
Relay Structure and Operating Principle
The basic principle behind a relay is the alteration of contact states in response to voltage (current), temperature, or light, depending on the type and intended application.
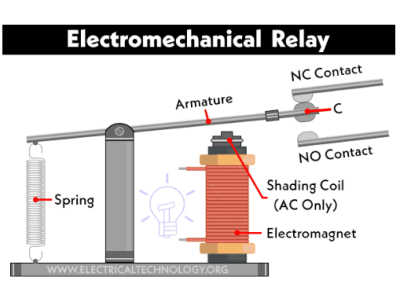
The contact group (CG) consists of metallic elastic plates, which may be equipped with springs. One side of the plates connects to the electrical circuit, while the other side contains the contacts, which can either be closed or open when the relay is off.
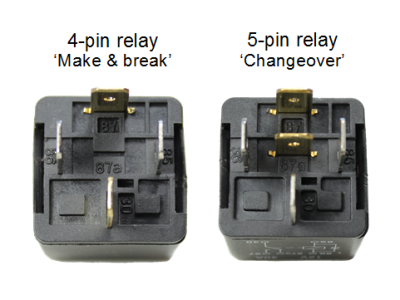
In the first case, they are called normally closed contacts, and in the second, normally open contacts. The contact group may have two contacts working on closure (or opening) or three (one common and one each for closing and opening), allowing for a switching mode.
A relay may have multiple contact groups of any type.
The most common type is the electromagnetic relay, where the change in contact positions is driven by a mechanical connection to an electromagnet, powered by either AC or DC voltage (current).
Relays can also be enhanced with additional features, such as a photo-sensitive element and an electric circuit to create a photo relay. Adding a microphone results in an acoustic relay, and a thermometer turns it into a thermistor relay. The latter can operate without electrical control, using bimetallic plates to bend under temperature changes, although this version lacks the adjustability and precision of electric relays.
Relay Applications and Uses
Let's break down the basics of relays:
Relay Components and Functioning:
A relay typically consists of contact groups controlled by an electromagnet. When electric current flows through the coil, the magnetic field changes the position of the armature, which is mechanically linked to the contact plates.Primary Purposes:
- Amplification: Small currents flowing through the coil control contacts that can switch much higher powers (like an amplifier).
- Signal Distribution: Multiple contact groups allow one signal to control several independent pathways (acting as a distributor).
- Inversion: Using normally closed contacts, applying voltage to the coil can cause the circuit to open (inversion).
- Galvanic Isolation: Since the control and switching parts of the relay are electrically separated, galvanic isolation between circuits is ensured.
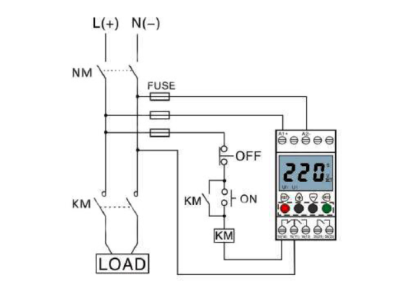
Thanks to their simplicity and reliability, relays are widely used in automation, protection systems, control systems, and signaling devices.
- AC vs. DC Relays:
In the context of physics, the direction of the magnetic field depends on the direction of the electrical current. With DC voltage, the magnetic field remains constant, keeping the armature always in a pulled-in state.
If AC voltage is used without modifications, the alternating magnetic field will cause the armature and contacts to vibrate. To avoid this, special design adjustments are made in AC relays to compensate for these fluctuations.
Technical Characteristics and Parameters
The contacts are a key component in any relay, determining its electrical capabilities. Some important characteristics of the contacts include the voltage and current ratings they can handle. Additionally, the switching time is a critical factor – relays are inherently inertial, and several design features contribute to this delay:
- Electromagnetic Inductance: When current is applied to the coil, the inductance of the electromagnet resists the rapid increase in current, delaying the magnetic field from developing. This also delays the armature’s movement.
- Inertia of the Contact Group: The mass of the contact group and armature also contributes to the delay in switching.
One variant is the reed relay, which is an electromechanical relay but lacks a core. The magnetic field directly affects the contact plates, which are sealed in a vacuum tube, providing high-speed operation. However, reed relays can only handle low switching power.
When choosing a relay, it's important to consider the coil voltage and current, as these can vary significantly depending on the relay type. Generally, the stronger the contact group, the more power is required to control it.
Other factors to consider include:
- Protection Class: Resistance to external factors such as dust and moisture.
- Safety Standards: Relays for use in hazardous environments require specific designs to ensure safety.
While these parameters may not be critical in standard applications, certain settings require strict compliance with safety and operational guidelines, especially when relays with exposed contacts are used in 110V networks.
By ensuring the correct specifications, relays provide a reliable and efficient solution for a wide variety of electrical and automation systems.