Building Surveillance Systems
Designing a reliable surveillance system begins with detailed project planning. This includes selecting the system type, determining equipment needs, and optimizing camera placement.
Key Steps in Building a Surveillance System
- Define Objectives: Establish the goals of the system-e.g., property monitoring, facial recognition, or perimeter control.
- Select System Type: Choose between analog and IP surveillance based on budget, complexity, and scalability.
- Choose Equipment: Identify the right cameras, recording devices, and power supplies.
- Plan Installation: Map out cable routes, camera placement, and integration with existing infrastructure.
Analog Surveillance Systems
Analog systems are cost-effective and simple to implement, making them ideal for:
- Residential use: Home or small business applications.
- Distant Monitoring: Using coaxial cables for short distances or twisted pair wiring with transmitters for extended ranges.
Advantages
- Affordability: Lower initial investment.
- Ease of Use: Simpler setup and maintenance.
Modern Analog Enhancements
Advanced analog technologies, such as AHD (Analog High Definition), now support high-resolution video, bridging the gap between affordability and quality.
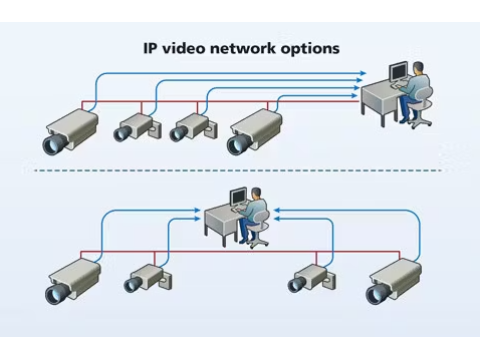
IP Surveillance Systems
IP systems are more flexible and scalable, suitable for large-scale or complex setups.
Advantages
- Scalability: Easily expand by adding cameras.
- Analytics: Built-in video analysis features.
- Remote Access: Seamless monitoring via the internet.
Network Planning
- Cabling: Use Ethernet (twisted pair) for connections under 328 feet (100 meters).
- Wireless: Ideal for areas where cabling is impractical.
- Bandwidth Management: Ensure the network can handle video traffic by calculating the required bitrate.
Bandwidth Calculation for IP Cameras
The following table provides approximate bandwidth requirements for different resolutions using the H.264 codec at 25 frames per second:
| Resolution | Bitrate (Mbps) |
|---|---|
| 720p | 1-2 Mbps |
| 1080p | 2-4 Mbps |
| 4K | 8-12 Mbps |
Installation Best Practices
- Cable Management: Use shielded cables for EMI-prone areas.
- Power Options: Opt for PoE (Power over Ethernet) to reduce wiring complexity.
- Equipment Placement: Centralize network switches for easy maintenance.
Conclusion
Whether analog or IP-based, the success of a surveillance system hinges on careful planning and implementation. Analog systems excel in simplicity and cost, while IP systems offer unparalleled flexibility and features, making them suitable for evolving security needs.