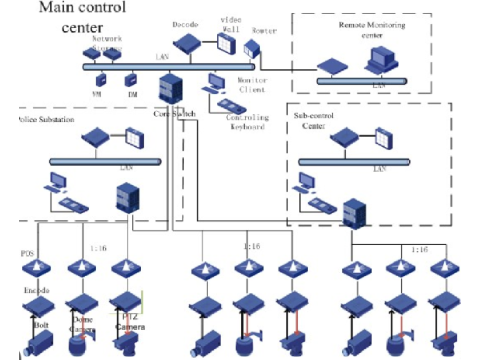
Writing a Technical Specification for Video Surveillance System Design
Creating a technical specification is a critical step in designing an effective video surveillance system. This document ensures both the customer and installer have a clear understanding of the project’s scope, requirements, and expectations. Below are the key components to include and steps to follow.
Key Elements to Address
1. Required Surveillance Zones
Define the areas that need monitoring and specify:
- Type of monitoring: Indoor, outdoor, or both.
- Coverage areas: Entrances, perimeters, parking lots, offices, etc.
- Expected outcomes: Identification, detection, or general observation.
2. Lighting Conditions
Establish whether artificial lighting is available for nighttime use. This affects camera requirements such as:
- Light sensitivity: Measured in lux for low-light conditions.
- Infrared (IR) capabilities: Necessary for dark environments.
3. Video Storage Requirements
Determine the required retention period for video archives, which depends on:
- Number of cameras.
- Recording resolution.
- Recording frame rate.
Example: A 30-day archive for 16 cameras recording at 1080p and 12 fps will require more storage than 7 days of lower-resolution recordings.
4. Access to Video Archives
Specify how users will access recordings:
- Local access: Via on-site monitors or recorders.
- Remote access: Through a local network or internet connection.
5. Video Quality and Recording Speed
Define the frame rate and resolution for recording.
- Lower frame rates (e.g., 12 fps) reduce storage needs without significantly compromising monitoring quality.
- Higher frame rates (e.g., 25 fps) may be required for high-traffic areas.
6. Tasks and Objectives for Each Zone
Define tasks such as:
- Identification: Recognizing individuals or vehicles.
- Detection: Noticing movement or intrusions.
- Recognition: Monitoring specific activities.
7. Special Requirements
List any unique needs, such as:
- Advanced video analytics (e.g., motion detection, facial recognition).
- Information security measures.
- User access controls.
Structuring the Technical Specification
The specification should be detailed and formatted to facilitate approval by both the client and the design organization.
Include the Following Information:
- Project Details: Name and address of the property, purpose of the system (asset protection, personnel monitoring, etc.).
- System Type: Specify analog or IP-based systems.
- Property Description: Size, layout, number of floors, and other relevant details.
- Operating Conditions: Environmental factors such as temperature ranges, humidity, and operating hours.
- Power Requirements: Define electrical needs and backup power solutions.
- Equipment Locations: Planned placement of servers, monitors, and recorders.
Importance of a Well-Defined Specification
For larger projects, creating a thorough technical specification is a time-intensive process but critical for:
- Avoiding disputes between the client and installer.
- Ensuring all parties understand the system’s requirements and objectives.
- Facilitating approvals and smooth project execution.
For small-scale projects, simplified documentation can suffice but should still cover essential requirements to prevent misunderstandings.
Conclusion
A well-crafted technical specification is the foundation of any successful video surveillance project. By detailing the system’s objectives, environmental conditions, and technical requirements, you ensure a smooth installation process and optimal performance.