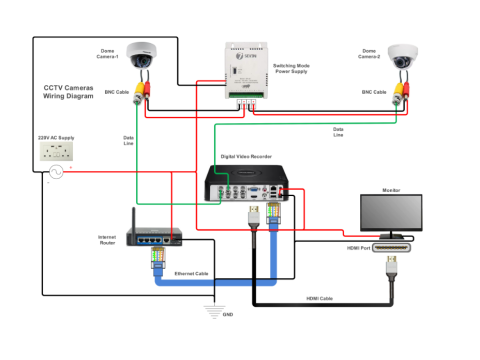
Surveillance Camera Connection Schemes
Modern surveillance systems use various methods to transmit video signals from cameras to monitoring devices like DVRs, NVRs, or TV screens. This guide explores two primary connection schemes: twisted pair and coaxial cable setups, detailing their applications and limitations.
1. Twisted Pair Connection
Overview:
Twisted pair cabling is widely used in modern surveillance setups due to its flexibility and reduced susceptibility to electromagnetic interference.
Connection Process:
- Signal Conversion: The analog signal from the camera is converted into a balanced (symmetrical) signal for transmission.
- Transmission: The signal is sent over the twisted pair cable.
- Reconversion: At the receiving end, the signal is converted back to its original form for display or recording.
Diagram:
Refer to Figure 1 to visualize a typical twisted pair connection for surveillance cameras.
2. Coaxial Cable Connection Schemes
Coaxial cables are a traditional choice for transmitting video signals due to their simplicity and durability. Below are various connection schemes using coaxial cables:
2.1 Direct Connection
- Description: The camera is directly connected to the monitoring device (e.g., DVR or monitor) via a coaxial cable.
- Limitations: Effective for distances of up to a few hundred feet, depending on the cable quality.
2.2 Connection with an Amplifier
- Purpose: Extends the transmission range to over 1,000 feet.
- Setup: An amplifier is installed between the camera and monitoring device to boost the signal.
2.3 High-Frequency Filter Setup
- Usage: Reduces high-frequency noise and improves image clarity.
- Limitations: Typically supports distances up to 500 feet.
2.4 Modulation and Demodulation (RF Transmission)
- Description: Converts the video signal into a high-frequency RF signal for improved transmission.
- Process:
- The camera's signal is modulated to a high-frequency RF format using a modulator.
- At the receiving end, a demodulator converts the RF signal back to its original format.
- Advantage: Better compatibility with TV systems.
2.5 Direct TV Connection
- Description: Connect the camera directly to a TV's antenna input using a modulator.
- Usage: Suitable for simple setups where real-time monitoring is the primary goal.
Tips for Effective Connection
- Cable Quality: Always use high-quality coaxial or twisted pair cables to ensure signal integrity.
- Distance Considerations: Use amplifiers or modulators for long-distance setups to prevent signal degradation.
- Interference Management: Avoid running surveillance cables parallel to power lines to minimize interference.
Conclusion
Choosing the right connection scheme depends on your surveillance system's requirements, such as distance, image quality, and compatibility. Coaxial and twisted pair cabling are both reliable options, with the latter gaining popularity for modern systems. By understanding these schemes, you can optimize your surveillance setup for maximum efficiency and reliability.