DIY Electrical Installation: Comprehensive Guide for Homes, Apartments, and Cottages
Introduction to DIY Electrical Installation
Embarking on DIY electrical installation projects in your home, apartment, or cottage is entirely feasible with the right knowledge and precautions. However, it requires a fundamental understanding of electricity, adherence to safety protocols, and compliance with electrical standards and regulations. This guide provides the essential theoretical information and practical advice needed to undertake electrical work safely and effectively.
Essential Knowledge for DIY Electrical Work
Before attempting any electrical installation, it’s crucial to grasp the basics of electricity, including the laws that govern it, the parameters and characteristics of electrical equipment, and the materials used in electrical installations. Familiarize yourself with the regulatory requirements outlined in standards such as the Russian "Rules for Electrical Installations" (PUE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, which modern PUE requirements closely align with.
Permitted DIY Electrical Tasks in the USA
In the USA, homeowners are allowed to perform certain electrical tasks without the need for permits or inspections, provided they comply with local building codes and safety regulations. Permissible tasks include:
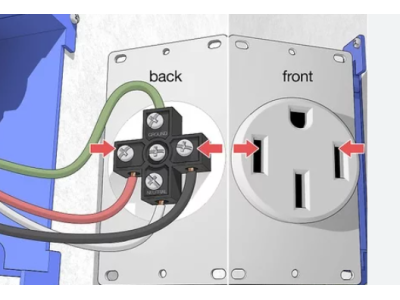
- Replacing or Repairing Outlets and Switches: Swapping out old outlets and switches with new ones.
- Repairing Sections of Electrical Wiring: Fixing or replacing damaged wiring within existing circuits.
- Installing New Light Fixtures, Outlets, and Switches: Adding new lighting fixtures or additional electrical outlets to existing circuits.
Other tasks, such as installing new circuits or significant electrical upgrades, typically require permits and must be performed by licensed electricians.
Safety and Electrical Compliance
When performing any electrical work, prioritize safety and compliance to prevent accidents and ensure the longevity and reliability of your electrical systems. Key safety measures include:
- Personal Safety: Always turn off the power at the main electrical panel before starting any work. Use an insulated screwdriver and tools with insulated handles to reduce the risk of electric shock.
- Electrical Safety: Ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated. Avoid overloading circuits by adhering to the rated capacity of breakers and outlets.
- Fire Safety: Use the correct wire gauge for your electrical load and ensure all connections are tight to prevent overheating and potential fires. Install appropriate circuit breakers and Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) where necessary.
Basic Safety Techniques
- De-Energize Circuits: Always disconnect power to the circuit you’re working on using the main breaker panel.
- Verify Power is Off: Use a non-contact voltage tester or multimeter to confirm that the circuit is de-energized before touching any wires.
- Use Insulated Tools: Employ tools with insulated handles to protect against accidental shocks.
- Work in a Dry Environment: Ensure your workspace is dry to minimize the risk of electric shock.
Electrical and Fire Safety Best Practices
To mitigate the risks associated with electrical work, adhere to the following best practices:
- Proper Wire Selection: Use wires with the appropriate insulation, material, and gauge to handle the intended electrical load.
- Quality Electrical Components: Invest in high-quality switches, outlets, and junction boxes rated for your electrical requirements.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all wire connections are tight and secure to prevent arcing and overheating.
- Protective Devices: Install circuit breakers and GFCIs to provide overcurrent protection and prevent electrical fires and shocks.
- Grounding: Properly ground all electrical systems to protect against electrical faults and reduce the risk of fire.
Planning Your DIY Electrical Project
Successful DIY electrical installation requires meticulous planning and adherence to standards. Follow these steps to ensure a safe and effective project:
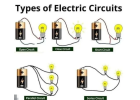
Design and Planning:
- Assess Needs: Determine the scope of your electrical project, including the number of outlets, switches, and fixtures you plan to install.
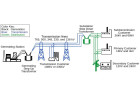
- Create a Diagram: Sketch a layout of your electrical system, indicating the placement of all components and the routing of wires.
- Check Codes: Review local electrical codes and regulations to ensure your project complies with all safety standards.
Gathering Materials:
- Electrical Tools: Ensure you have the necessary tools, including wire strippers, screwdrivers, voltage testers, and multimeters.
- Quality Components: Purchase high-quality electrical outlets, switches, wiring, and protective devices that meet the required specifications.
Execution:
- Follow the Diagram: Adhere strictly to your electrical diagram to ensure proper installation and functionality.
- Secure Connections: Make sure all electrical connections are tight and properly insulated to prevent hazards.
- Double-Check Work: Before restoring power, review all connections and installations to ensure they are correct and safe.
Testing and Verification:
- Power On: Carefully restore power to the electrical system.
- Test Functionality: Verify that all installed outlets, switches, and fixtures operate correctly.
- Monitor for Issues: Keep an eye out for any signs of malfunction, such as flickering lights or tripped breakers, and address them promptly.
When to Seek Professional Help
While DIY electrical work can be rewarding and cost-effective, certain tasks should always be handled by licensed electricians to ensure safety and compliance:
- Installing New Circuits: Adding new circuits to your electrical panel often requires professional expertise.
- Upgrading Electrical Panels: Modernizing or expanding your electrical panel should be done by professionals to meet current safety standards.
- Handling Complex Wiring: Projects involving complex wiring configurations or high-voltage installations necessitate professional intervention.
Conclusion
DIY electrical installation in your home, apartment, or cottage is achievable with the right knowledge, tools, and adherence to safety protocols. By understanding the basics of electricity, following safety guidelines, and complying with electrical standards, you can successfully undertake a variety of electrical projects. However, always recognize your limits and seek professional help for complex or high-risk tasks to ensure a safe and reliable electrical system.
At safsale.com, we provide a wide range of high-quality electrical components and tools to support your DIY projects. Equip yourself with the right materials and knowledge to create a safe and efficient electrical system in your living space. For more information and to explore our selection of electrical products, visit safsale.com